The Good News About Fish Oil
Author: Dr. Stephen Chaney
 High blood pressure or hypertension is a major problem in this country. Over 60% of Americans have high blood pressure. Only 47% of those with hypertension are adequately controlled. 20% of them don’t even know that they have high blood pressure.
High blood pressure or hypertension is a major problem in this country. Over 60% of Americans have high blood pressure. Only 47% of those with hypertension are adequately controlled. 20% of them don’t even know that they have high blood pressure.
In this case, ignorance is definitely not bliss. That’s because high blood pressure significantly increases the risk of stroke, heart attacks and congestive heart failure.
The causes of high blood pressure are many. Genetics, obesity, lack of exercise, sodium, alcohol, saturated fats and too few fresh fruits and vegetables all play a role. Age also plays a role. As we age, our blood vessels become less flexible and our blood pressure rises by about 0.6 mm Hg per year.
Medications can help, but many of them have significant side effects and often aren’t fully effective in controlling blood pressure. That’s why natural approaches are so important.
Because there are so many causes of hypertension, natural approaches for lowering your blood pressure are not simple. Natural approaches start with weight loss, restricting sodium intake, increasing physical activity, moderating alcohol intake and something called the DASH diet. In short, there is not just one simple change that you can make that will totally eliminate hypertension. It requires a complete lifestyle change.
That’s why the latest study on the effect of omega-3s on blood pressure is so exciting. If the headlines are true, adding omega-3s to your diet may be one of the most effective things you can do to lower your blood pressure naturally. So let’s examine the study to see if the headlines are accurate.
How Was The Study Designed?
This study (Miller et al, American Journal of Hypertension, doi:10.1093/ajh/hpu024) was a very large, well designed study. It is a meta-analysis of 70 randomized, placebo controlled clinical studies. Key characteristics of these studies were:
- The mean study duration was 69 days. That means these beneficial effects occur relatively quickly.
- The mean EPA + DHA dose was 3.8 g/day (range = 0.2 – 15 g/day). A wide range of doses was included.
- The EPA & DHA came from all sources (seafood, EPA+DHA fortified foods, fish oil, algal oil, and purified ethyl esters. The source did not affect the outcome.
- Olive oil was the most commonly used placebo, with omega-6 vegetable oils being used as placebos in a few studies. The choice of placebo did not affect the outcome.
- None of the people in these studies were taking blood pressure lowering medications. That means these studies were specifically designed to see whether omega-3s lowered blood pressure, not whether they had any additional benefit for people already taking medications. This is important because if you only focus on groups who are already taking multiple medications, you tend to obscure the beneficial effects of omega-3s (see my recent Health Tip “Is Fish Oil Really Snake Oil?”)
Do Omega-3s lower Blood Pressure?
 The authors of the study reported that:
The authors of the study reported that:
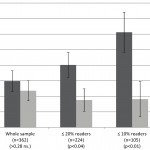
- Compared to placebo, EPA+DHA reduced systolic blood pressure (that’s the upper reading) by 1.52 mm Hg and diastolic blood pressure (that’s the lower reading) by 0.99 mm Hg.
- When they looked at those participants who already had high blood pressure, the numbers were even more impressive – a 4.51 mm Hg decrease in systolic blood pressure and a 3.05 mm Hg decrease in diastolic blood pressure. That’s important because for each 2 mm Hg reduction in blood pressure there is a 6% decrease in stroke mortality, a 4% decrease in heart disease mortality, and a 3% decrease in total mortality.
More to the point, the authors of the study concluded that “A decrease of 4.51 mm Hg in systolic blood pressure among those with high blood pressure could help an individual avoid having to take medication to control blood pressure levels”.
- When they looked at the study participants who had normal blood pressure the numbers were still significant – a 1.25 mm Hg decrease in systolic blood pressure and a 0.62 decrease in diastolic blood pressure. The authors pointed out that this could prevent, or at least delay, the age-related progression towards hypertension.
- The effect of omega-3s on systolic blood pressure (4.51 mm Hg decrease) was comparable to the most successful lifestyle interventions – 3-10 mm Hg decrease for 10 pound weight loss, 4-9 mm Hg decrease for increased physical activity, 2-8 mm Hg decrease for sodium restriction, and 2-4 mm Hg for decreased alcohol consumption.
- A dose of at least 1 gm/day of EPA+DHA was required for a significant decrease in systolic blood pressure, and a dose of over 2 gm/day was required for a significant decrease in both systolic and diastolic blood pressure
While this is a single study, it is consistent with a number of previous studies in this area. Based on the existing body of literature I would recommend omega-3s as part of a holistic approach for keeping your blood pressure under control.
The Bottom Line:
1) A recent meta-analysis of 70 published clinical studies (AJH, doi: 10.1093/ajh/hpu024) has shown fairly convincingly that omega-3 fatty acids are effective at lowering blood pressure. Moreover, this study is consistent with a number of previous studies. The evidence appears to be strong enough for omega-3s to be considered as part of a holistic approach to keeping your blood pressure under control.
2) If you already have high blood pressure, you should know that omega-3s caused blood pressure to decrease by 4.51 mm Hg in people like you. The authors of the study concluded that this decrease in blood pressure is large enough that some people may be able to avoid blood pressure medicines entirely. For others addition of omega-3s to their diet will likely allow their physicians to reduce the dose of medications required to keep their blood pressure under control – thus minimizing the side effects of the medications.
3) If you already have slightly elevated blood pressure that has not yet progressed to clinical hypertension, you should know that omega-3s also give a modest decrease in blood pressure in people like you. The authors of the study concluded that this decrease was enough to prevent or delay the age-related onset of hypertension.
4) The effect of omega-3s on reducing blood pressure is equivalent to the most successful lifestyle changes (weight loss, increased physical activity, sodium restriction and alcohol moderation). That doesn’t mean that you should pop fish oil pills and forget the other lifestyle changes. The idea is to combine as many of those lifestyle changes as possible so that you may never have to worry about high blood pressure again.
5) You need at least 1 gm/day of EPA+DHA to reduce systolic blood pressure and more than 2 gm/day to reduce both systolic and diastolic blood pressure.
6) Contrary to the hype you may have been reading elsewhere, the source of EPA+DHA didn’t matter. The only caveat is that many people really struggle with trying to get 1-2 gm/day of EPA+DHA from fish. It’s a bit too much of a good thing.
7) Don’t think of hypertension as a “Do it yourself” project. Hypertension is a silent killer. It’s one of those diseases where the first symptom is often sudden death – or, even worse, a life that is no longer worth living. Work with your physician. Let them help you find the right balance between lifestyle changes (including omega-3s) and medications to keep your blood pressure under control.
These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This information is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any disease.