Which Diets Are Best For Your Health?
Author: Dr. Stephen Chaney
 Is it hot enough yet? I’m not going to take a stand in the global warming debate. But I will say this summer has been extraordinarily hot – even for North Carolina.
Is it hot enough yet? I’m not going to take a stand in the global warming debate. But I will say this summer has been extraordinarily hot – even for North Carolina.
So, what can we do about it? I will list some options below. But with “tongue in cheek” I will give voice to both sides of each option.
- We can elect politicians of our choice and hope they have the wisdom to balance reductions in global warming with the energy needs of our country – but there has been little evidence of that wisdom from either end of the political spectrum.
- We can purchase electric cars – despite their cost, limited range, and long refueling times.
- We can recycle – even though most of what we recycle ends up in regular trash.
- We can turn up our thermostats in summer and down in winter – and choose to swelter in summer and shiver in winter.
- We can change our diet – but wait. Could this be a win no matter what our views are on climate change? Could the same diets that are better for the planet also be better for our health?
That is the hypothesis today’s study (K. O’Malley et al, The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 117: 701-708, 2023) set out to test.
How Was The Study Done?
 The investigators analyzed 24-hour dietary recall data from 16,412 participants from the 2005 – 2010 NHANES survey. NHANES (National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey) is an ongoing, nationally representative, survey to measure the health and nutrition status of the US population. This investigation used data collected between 2005 and 2010.
The investigators analyzed 24-hour dietary recall data from 16,412 participants from the 2005 – 2010 NHANES survey. NHANES (National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey) is an ongoing, nationally representative, survey to measure the health and nutrition status of the US population. This investigation used data collected between 2005 and 2010.
The dietary data were used to categorize the intake of individual participants into different diets as follows:
- Vegan – plant foods only.
- Vegetarian – includes eggs and dairy but excludes meat.
- Pescatarian – includes fish as the major source of meat.
- Paleo – excludes grains, legumes, and dairy.
- Keto – excludes grains, legumes, fruits, and starchy vegetables.
- Omnivore – Any diet not included in the categories above.
The omnivore diet was further divided to identify people following the DASH and Mediterranean diets.
The environmental impact of each diet was calculated based on the amount of CO2 and methane produced in the production of the foods included in the diet.
The impact on our health of each diet was calculated based on the Alternative Healthy Eating Index.
- The Healthy Eating Index was first developed in 1995 as tool to gauge how well a diet followed the Dietary Guidelines for Americans established by the Department of Health & Human Services and the USDA.
- The Alternative Healthy Eating Index was first developed in 2002 to include a wider range of foods and to better predict the effect of diet on chronic diseases based on clinical studies of health outcomes.
- Each of these indices are regularly updated as more data become available.
Which Diets Are Best For the Planet?
I have put the data in a graphical format, so it is easier to visualize.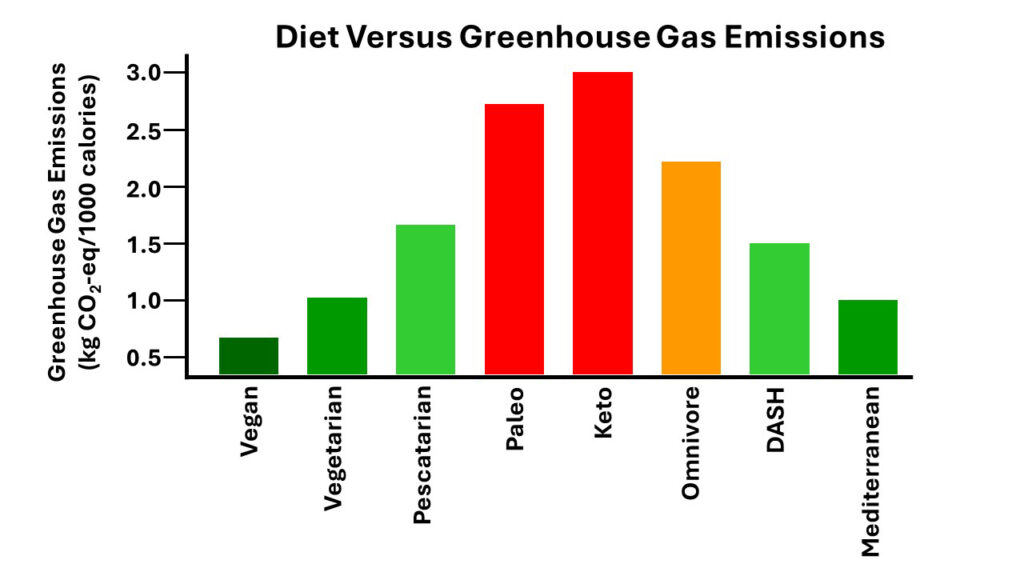 The vertical axis is greenhouse gas emissions expressed as kg of CO2 equivalents per 1,000 calories (The term CO2 equivalents is used because cows and sheep produce methane which is a much more potent greenhouse gas than CO2). Lower is better.
The vertical axis is greenhouse gas emissions expressed as kg of CO2 equivalents per 1,000 calories (The term CO2 equivalents is used because cows and sheep produce methane which is a much more potent greenhouse gas than CO2). Lower is better.
On the horizontal axis the diets from left to right are vegan, vegetarian, pescatarian, paleo, keto, omnivore, DASH, and Mediterranean. The diets with the least greenhouse gas emissions are shown in green (the greener the better), and the diets with the most greenhouse gas emissions are shown in orange and red.
Which Diets Are Best For Your Health?
Once again, I have chosen a graphical representation.
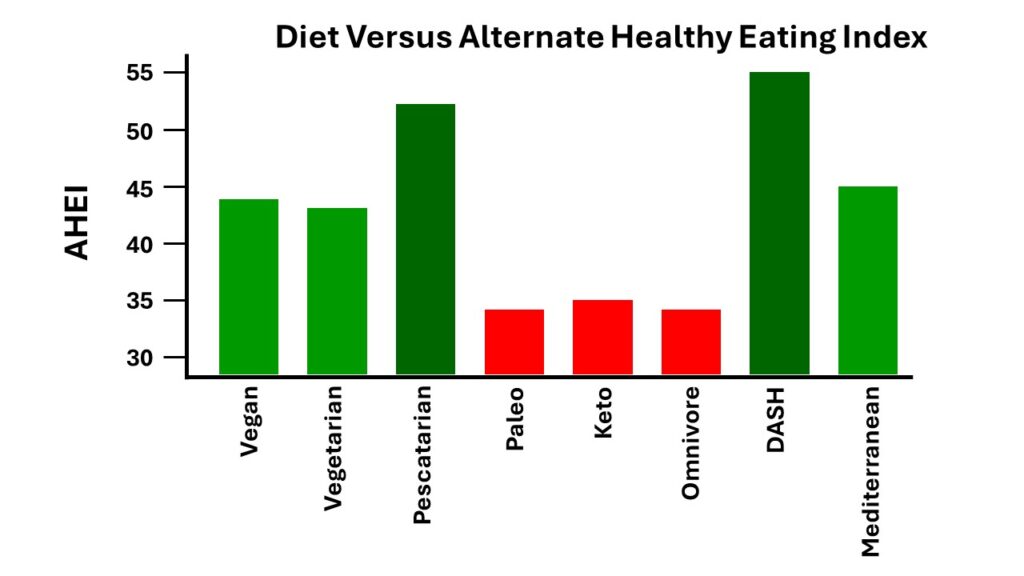 The vertical axis is the Alternative Healthy Eating Index. In this case, higher is better.
The vertical axis is the Alternative Healthy Eating Index. In this case, higher is better.
The color score is the same as above. However, I would note that:
- Fish is the main animal protein source in the pescatarian diet. I suspect that the vegan and vegetarian diets would score just as high as the pescatarian diet in the Alternative Healthy Eating Index if an omega-3 supplement was taken along with the diets.
- The Alternative Healthy Eating Index is weighted heavily on clinical studies showing that a particular diet reduces the risk of heart disease, diabetes, and/or cancer. That is likely why the DASH diet ranks so high. It was designed to decrease the risk of hypertension. Because of that there have been dozens of studies showing it reduces the risk of strokes and heart attacks.
The available evidence suggests that the Mediterranean diet is just as effective as the DASH diet at reducing the risk of strokes, heart attacks, and diabetes. But we do not yet have as many studies looking at the effect of the Mediterranean diet on those diseases. Based on the currently available evidence, I consider the Mediterranean diet to be just as healthy as the DASH diet.
Finally, I would like to point out the obvious. This and other studies show that the same diets that are good for the planet are good for our health.
For example, the authors estimated:
- For any given day, if a third of omnivores in the United States switched to a vegetarian diet, it would be equivalent to eliminating 340 million passenger miles in gas-powered vehicles.
- If this change were implemented year-round, it would amount to almost 5% of the reductions in greenhouse gas emissions needed to meet the original US targets in the Paris accords.
- For those omnivores who made the switch to a vegetarian diet, it would improve diet quality by 6%.
Of course, if all omnivores in the United States switched to a vegetarian diet, these percentages would be tripled, but that is wildly unrealistic.
What Does This Study Mean For You?
 The take home lesson from this study is clear.
The take home lesson from this study is clear.
If your primary concern is climate change, choose the planet-healthy diet that best fits your food preferences and lifestyle. [The ones with the lowest greenhouse gas emissions are shown in green in the first graph above – the greener, the better.] Any of these diets will also be good for your health.
If your primary concern is health, choose the healthy diet that best fits your food preferences and lifestyle. [The ones with the highest Alternate Healthy Eating Index are shown in green in the second graph above – the greener, the better.] Any of these diets will also be good for the planet.
The Bottom Line
A recent study compared 8 popular diets (vegan, vegetarian, pescatarian, paleo, keto, omnivore, DASH, and Mediterranean) with respect to their impact on the environment and on your health.
The results were clear-cut. The diets that were best for the planet were best for your health and vice-versa.
For example, the authors estimated:
- For any given day, if a third of omnivores in the United States switched to a vegetarian diet, it would be equivalent to eliminating 340 million passenger miles in gas-powered vehicles.
- If this change were implemented year-round, it would amount to almost 5% of the reductions in greenhouse gas emissions needed to meet the original US targets in the Paris accords.
- For those omnivores who made the switch to a vegetarian diet, it would improve diet quality by 6%.
For more details about this study and what it means for you read the article above.
These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This information is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
______________________________________________________________________________
My posts and “Health Tips From the Professor” articles carefully avoid claims about any brand of supplement or manufacturer of supplements. However, I am often asked by representatives of supplement companies if they can share them with their customers.
My answer is, “Yes, as long as you share only the article without any additions or alterations. In particular, you should avoid adding any mention of your company or your company’s products. If you were to do that, you could be making what the FTC and FDA consider a “misleading health claim” that could result in legal action against you and the company you represent.
For more detail about FTC regulations for health claims, see this link.
https://www.ftc.gov/business-guidance/resources/health-products-compliance-guidance
About The Author
 Dr. Chaney has a BS in Chemistry from Duke University and a PhD in Biochemistry from UCLA. He is Professor Emeritus from the University of North Carolina where he taught biochemistry and nutrition to medical and dental students for 40 years. Dr. Chaney won numerous teaching awards at UNC, including the Academy of Educators “Excellence in Teaching Lifetime Achievement Award”. Dr Chaney also ran an active cancer research program at UNC and published over 100 scientific articles and reviews in peer-reviewed scientific journals. In addition, he authored two chapters on nutrition in one of the leading biochemistry text books for medical students.
Dr. Chaney has a BS in Chemistry from Duke University and a PhD in Biochemistry from UCLA. He is Professor Emeritus from the University of North Carolina where he taught biochemistry and nutrition to medical and dental students for 40 years. Dr. Chaney won numerous teaching awards at UNC, including the Academy of Educators “Excellence in Teaching Lifetime Achievement Award”. Dr Chaney also ran an active cancer research program at UNC and published over 100 scientific articles and reviews in peer-reviewed scientific journals. In addition, he authored two chapters on nutrition in one of the leading biochemistry text books for medical students.
Since retiring from the University of North Carolina, he has been writing a weekly health blog called “Health Tips From the Professor”. He has also written two best-selling books, “Slaying the Food Myths” and “Slaying the Supplement Myths”. And most recently he has created an online lifestyle change course, “Create Your Personal Health Zone”. For more information visit https://chaneyhealth.com.
For the past 45 years Dr. Chaney and his wife Suzanne have been helping people improve their health holistically through a combination of good diet, exercise, weight control and appropriate supplementation.



