Preventing & Healing Repetitive Strain Injuries – Part 2
Author: Julie Donnelly, LMT
 In part I of this series we explored “how” muscles cause joint pain and prevent us from moving easily and without pain. In Part II we’ll take a look at the “why.”
In part I of this series we explored “how” muscles cause joint pain and prevent us from moving easily and without pain. In Part II we’ll take a look at the “why.”
When a person can’t freely move a joint they are frequently told they need to strengthen the muscle that moves the joint, but this is often a serious misconception. Let’s look at this further so it will become clear.
Most people have heard the term Repetitive Strain Injury (RSI), but they don’t have a clear concept of how that affects them on a daily basis.
Repetitive Strain Injuries (RSIs)
Repetitive strain injuries happen when a muscle does the same movement over and over, causing the muscle to develop an excess of Hydrogen ions (H+), which is a part of lactic acid. Lactic acid was once thought to be the “bad guy” that created spasms/knots in your muscles. Then research showed that lactic acid has two components, one is called lactate and it is an important piece of energy production, and the other is H+, which is the acid byproduct of energy production and is the cause of the spasms.
Your body has the ability to flush out H+, but if you are exercising, or repetitively doing the same movement, you are creating more H+ than your body can eliminate. The scales tip and the excess lactic acid will cause the muscle fibers to contract into a spasm. The spasm is usually formed slowly so you don’t notice it until it is so evolved that the fibers are twisted into a knot and are putting a strain on the insertion point at the joint.
Strengthening vs Lengthening
When you can’t bend a joint, such as your elbow, you are often told to strengthen the muscle that pulls on the joint, in this case, the biceps. However, you actually need to lengthen your triceps.
In fact, I tell my clients to first look at the area where they are feeling pain, and then find out which muscle inserts at that point. If you can’t bend a joint, I tell people to look at what muscles should be stretching to enable the joint to move. The likelihood is great that the tight muscle is the cause your problem.
You’ll be amazed at how quickly you will regain full range-of-motion when you release the “straps that are holding you bound” by lengthening the contracted muscles.
Another piece of the strengthening misconception occurs when a person feels they are losing power in their muscle. Many times the person isn’t feeling any pain in their body, just a general feeling of loss of strength. You know you are exercising, but still you aren’t as strong as you were, so you feel you need to increase your strengthening exercises.
How Strengthening Can Hurt Your Muscles
To demonstrate this topic we’ll use the biceps of the upper arm as our example. I do a lot of my work with endurance athletes, athletes who are power lifters or simply individuals who exercise to the extreme. I’ve seen how they are in severe pain, sometimes to the point where they can’t do even the simplest movements without having not only pain but also losing power.
Often they lose power because the pain is too sharp when they go to lift the weight, or do pull ups. Other times they just feel like they are having weakness in the muscle, which makes them more determined to exercise that muscle even more. What has happened is the muscle is now too short to have any pulling power.
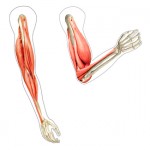
 Look at the graphic to the left. Many endurance athletes look just like this drawing, and some people think this is the picture of strength. However what is happening is the biceps muscles have been shortened to the point where he can’t completely straighten his arm, so he has actually lost power.
Look at the graphic to the left. Many endurance athletes look just like this drawing, and some people think this is the picture of strength. However what is happening is the biceps muscles have been shortened to the point where he can’t completely straighten his arm, so he has actually lost power.
But you don’t need to be an endurance athlete to have this experience. If any muscle in your body is shortened by spasms, whether they are from doing a repetitive movement or from exercise, you will also lose strength in those muscle fibers.
Consider this: if you couldn’t move your body, but you wanted to pull a heavy object toward you, you would stretch your arm out all the way and then pull on the object. If you stepped closer to the object so your arm is now bent, you can see that you wouldn’t have as much strength to move the heavy object. In the same way, when a muscle is already shortened by either a spasm or a static contraction, it won’t have the full pulling power it needs to function properly. You need to lengthen the fibers to their optimal length so they can pull with full strength.
You stretch, but often people will complain that the muscles aren’t stretching, or they hurt worse after the stretch than they did before stretching. This brings us to the “stretching misconception,” which will be explained in Part III of this trilogy.
Julie Donnelly is an internationally respected muscular therapist specializing in the treatment of chronic pain and sports injuries. She has co-authored several self-treatment books, including The 15 Minute Back Pain Solution, Treat Yourself to Pain-Free Living and Carpal Tunnel Syndrome-What You Don’t Know CAN Hurt You. Julie is also the co-developer of TriggerPoint Yoga. She teaches Julstro self-treatment workshops nationwide and is a frequent presenter at Conventions and Seminars. Julie may be contacted through her websites: http://www.julstro.com and http://www.TriggerPointYoga.com.
© Julie Donnelly 2013
These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This information is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any disease.