What Does This Study Mean For Your Children?
Author: Dr. Stephen Chaney
 It is back to school time again. If you have children, you are probably rushing around to make sure they are ready.
It is back to school time again. If you have children, you are probably rushing around to make sure they are ready.
- Backpack…Check.
- Books…Check
- School supplies…Check
- Omega-3s…???
Every parent wants their child to do their best in school. But do they need omega-3s to do their best? I don’t need to tell you that question is controversial.
Some experts claim that omega-3 supplementation in children improves their cognition. [Note: Cognition is defined as the mental action or process of acquiring knowledge and understanding through thought, experience, and the senses. In layman’s terms that means your child’s ability to learn.]
Other experts point out that studies in this area disagree. Some studies support these claims. Others don’t. Because the studies disagree these experts conclude there is no good evidence to support omega-3 supplementation in children.
The authors of this study (ISM van der Wurff et al, Nutrients, 12: 3115, 2020) took a different approach. They asked why these studies disagreed. They hypothesized that previous studies disagreed because there is a minimal dose of omega-3s needed to achieve cognitive benefits in children. In short, they were asking how much omega-3s do children need.
They based their hypothesis on recent studies showing that a minimum dose of omega-3s is required to show heart health benefits in adults.
What Have We Learned From Studies on Omega-3s And Heart Health?
 The breakthrough in omega-3/heart health studies came with the development of something called the omega-3 index. Simply put, omega-3s accumulate in our cell membranes. The omega-3 index is the percent omega-3s in red blood cell membranes and is a good measure of our omega-3 status.
The breakthrough in omega-3/heart health studies came with the development of something called the omega-3 index. Simply put, omega-3s accumulate in our cell membranes. The omega-3 index is the percent omega-3s in red blood cell membranes and is a good measure of our omega-3 status.
Once investigators began measuring the omega-3 index in their studies and correlating it with heart health, it became clear that:
- An omega-3 index of ≤4% correlated with a high risk of heart disease.
- An omega-3 index of ≥8% correlated with a low risk of heart disease.
- Most Americans have an omega-3 index in the 4-6% range.
- Clinical studies in which participants’ omega-3 index started in the low range and increased to ~8% through supplementation generally showed a positive effect of omega-3s on reducing heart disease risk. [I say generally because there are other factors in study design that can obscure the effect of omega-3s.]
This is the model that the authors adopted for their study. They asked how much omega-3s do children need to show a positive effect of omega-3s on their cognition (ability to learn).
How Was The Study Done?
 The authors included 21 studies in their analysis that met the following criteria:
The authors included 21 studies in their analysis that met the following criteria:
- All studies were placebo controlled randomized clinical trials.
- The participants were 4-25 years old and had not been diagnosed with ADHD.
- Supplementation was with the long-chain omega-3s DHA and/or EPA.
- The trial assessed the effect of omega-3 supplementation on cognition.
I do not want to underestimate the difficulties the authors faced in their quest. The individual studies differed in:
- The dose of omega-3s.
-
- The relative amount of DHA and EPA.
-
- Whether omega-3 index was measured. Only some of the studies measured fatty acid levels in the blood. The authors were able to calculate the omega-3 index in these studies.
- How cognition (ability to learn) was measured.
- The age of the children.
-
- 20 of the studies were done with children (4-12 years old) or late adolescents (20-25 years old).
-
- Only one study was done on early to middle adolescents (12-20 years old).
- All these variables influence the outcome and could obscure the effect of omega-3s on cognition.
In short, determining the omega-3 dose-response for an effect on cognition was a monumental task. It was like searching for a needle in a haystack. These authors did a remarkable job.
How Much Omega-3s Do Children Need?
 Here is what the scientists found when they analyzed the data:
Here is what the scientists found when they analyzed the data:
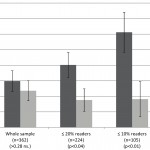
- 60% of the studies in which an omega-3 index of ≥6% was achieved showed a beneficial effect of omega-3 supplementation on cognition (ability to learn) compared to 20% of the studies that did not achieve an omega-3 index of 6%.
-
- That is a 3-fold difference in effectiveness once a threshold of 6% omega-3 index was reached.
- 50% of the studies in which a dose of ≥ 450 mg/day of DHA + EPA was used showed a beneficial effect of omega-3 supplementation on cognition (ability to learn) compared to 25% of the studies that used <450 mg/day DHA + EPA.
-
- That is a 2-fold difference in effectiveness once a threshold of 450 mg/day DHA + EPA was given.
The authors concluded, “Daily supplementation of ≥450 mg/day DHA and/or EPA and an increase in the omega-3 index to >6% makes it more likely to show efficacy [of omega-3s] on cognition (ability to learn) in children and adolescents.”
What Does This Study Tell Us?
 It is important to understand what this study does and does not tell us.
It is important to understand what this study does and does not tell us.
This study does not:
- Prove that omega-3 supplementation can improve cognition (ability to learn) in children and adolescents.
- Define optimal levels of DHA + EPA.
- Tell us whether DHA, EPA, or a mixture is better.
It was not designed to do any of these things. It was designed to give us a roadmap for future studies. It tells us how to design studies that can provide definitive answers to these questions.
This study does:
- Define a threshold dose of DHA + EPA for future studies (450 mg/day).
- Tells us how to best use the omega-3 index in future studies. To obtain meaningful results:
-
- Participants should start with an omega-3 index of 4% or less.
-
- Participants should end with an omega-3 index of 6% or greater.
- In my opinion, future studies would also be much more effective if scientists in this area of research could agree on a single set of cognitive measures to be used in all subsequent studies.
In short, this study provides critical information that can be used to design future studies that will be able to provide definitive conclusions about omega-3s and cognition in children.
What Does This Study Mean For Your Children?
 As a parent or grandparent, you probably aren’t interested in optimizing the design of future clinical studies. You want answers now.
As a parent or grandparent, you probably aren’t interested in optimizing the design of future clinical studies. You want answers now.
Blood tests for omega-3 index are available, but they are not widely used. And your insurance may not cover them.
So, for you the most important finding from this study is that 450 mg/day DHA + EPA appears to be the threshold for improving a child’s cognition (their ability to learn).
- 450 mg/day is not an excessive amount. The NIH defines adequate intakes for omega-3s as follows:
- 4-8 years: 800 mg/day
- 9-13 years: 1 gm/day for females, 1.2 gm/day for males
- 14-18 years: 1.1 gm/day for females and 1.6 gm/day for males.
- With at least 10% of that coming from DHA + EPA
Other organizations around the world recommend between 100 mg/day and 500 mg/day DHA + EPA depending on the age and weight of the child and the organization.
- Most children need supplementation to reach adequate omega-3 intake. The NIH estimates the average child only gets around 40 mg/day omega-3s from their diet. No matter which recommendation you follow, it is clear that most children are not getting the recommended amount of DHA + EPA in their diet.
- Genetics.
- Diet.
- Environment.
- The value placed on learning by parents and peers.
Supplementation is just one factor in your child’s ability to learn. But it is one you can easily control. . And if your child is like most, he or she is probably not getting enough omega-3s in their diet.
The Bottom Line
It is back to school time again. Every parent wants their child to do their best in school. But do they need omega-3s to do their best? I don’t need to tell you that question is controversial.
Some studies support these claims, but others don’t. Because the studies disagree some experts conclude there is no good evidence to support omega-3 supplementation in children.
The authors of a recent study took a different approach. They asked why these studies disagreed. They hypothesized that previous studies disagreed because there was a minimal dose of omega-3s needed to achieve cognitive benefits in children. They asked how much omega-3s children need.
They analyzed the data from 21 previous studies looking at the effect of omega-3 supplementation on cognition (ability to learn) in children and adolescents. Their analysis showed:
- 60% of the studies in which an omega-3 index of ≥6% was achieved showed a beneficial effect of omega-3 supplementation on cognition (ability to learn) compared to 20% of the studies that did not achieve an omega-3 index of 6%.
-
- That is a 3-fold difference in effectiveness once a threshold of 6% omega-3 index was reached.
- 50% of the studies in which a dose of ≥ 450 mg/day of DHA + EPA was used showed a beneficial effect of omega-3 supplementation on cognition (ability to learn) compared to 25% of the studies that used <450 mg/day DHA + EPA.
-
- That is a 2-fold difference in effectiveness once a threshold dose of 450 mg/day DHA + EPA was given.
The authors concluded, “Daily supplementation of ≥450 mg/day DHA + EPA and an increase in the omega-3 index to >6% makes it more likely to show efficacy [of omega-3s] on cognition (ability to learn) in children and adolescents.”
For more details on the study and what it means for your children and grandchildren, read the article above.
These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This information is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.