What Does This Mean For You?
Author: Dr. Stephen Chaney
 If you’ve ever traveled the subway system in London, you can’t have missed the “Mind the Gap” signs warning not to put your foot in the gap between the subway and the platform.
If you’ve ever traveled the subway system in London, you can’t have missed the “Mind the Gap” signs warning not to put your foot in the gap between the subway and the platform.
That warning is more important than ever in an age where people look at their cell phones rather than where they are walking. Of course, if they are looking at their cell phones, they might miss the sign and…
But today’s “Health Tip” is not about subway gaps. It’s about a far more important gap – the gap between our healthspan (how many years we enjoy good health) and our lifespan (how many years we live).
A recent study (L Gimeno et al, The Journals of Gerontology, Series B, 79(8), gbae113, 2024) suggesting that our healthy years are getting shorter caught my attention.
All of us imagine that our golden years will be ones of vibrant health. We’ll travel to exotic places. We’ll take long walks in the mountains. We’ll play with our grandchildren. Life will be wonderful.
But if this study is correct, none of that will happen for many young Americans. They will be too frail and sick to enjoy their golden years. They will be surviving rather than thriving.
So, in today’s “Health Tips From the Professor” I will review the study and tell you what it means for you.
How Was The Study Done?
 The investigators used data on 114,526 adults >50 (average age = 63) from developed countries (the United States, England, and continental Europe). Specifically, they used data from people who participated in the Healthy and Retirement Study (26,939 people in the United States), the English Longitudinal Study on Ageing (14,992 people in England), and the Survey of Health, Ageing, and Retirement (72,595 people in continental Europe) between 2004 and 2018.
The investigators used data on 114,526 adults >50 (average age = 63) from developed countries (the United States, England, and continental Europe). Specifically, they used data from people who participated in the Healthy and Retirement Study (26,939 people in the United States), the English Longitudinal Study on Ageing (14,992 people in England), and the Survey of Health, Ageing, and Retirement (72,595 people in continental Europe) between 2004 and 2018.
These surveys collected data on health-related outcomes every 2 years. The outcomes measured were:
- Six activities of daily living (ADLs) such as eating, bathing, and walking.
- Four instrumental activities of daily living (IADLs) related to essential tasks such as grocery shopping or preparing a hot meal.
- Seven measures of mobility difficulties and motor coordination tasks such as walking one block, lifting 10 pounds, or picking up a small coin from a flat surface.
The assumption was that the severity of limitations was ADL > IADL > mobility difficulties. This is based on previous research showing that a person with ADL limitations is likely to have IADL limitations and mobility difficulties. And a person with IADL limitations is likely to have mobility difficulties. Based on this assumption, they classified participants in this study into 4 disability categories:
- Mild disability: ≥1 IADL limitations and any number of mobility difficulties.
- Moderate disability: 1-2 ADL limitations with any number of IADL limitations and mobility difficulties.
- Severe disability: ≥3 ADL limitations with any number of IADL limitations and mobility difficulties.
The study also measured the prevalence (percent of the population) with:
- Obesity
- Heart disease.
- Diabetes
- Cancer
- Lung disease.
- High blood pressure.
- High cholesterol.
Finally, the study also measured grip strength because loss of grip strength is considered an indicator of future disabilities.
The unique feature of this study is it compared the health and disability of people who were at the same age when tested but were born in different decades ranging from 1925 to 1955.
Because of the rapid change in diet and lifestyle following World War II, the health and disability of people born in the 1936-1945 decade encompassing World War II was used as the standard to which all other decades were compared.
Are Our Healthy Years Getting Shorter?
Some of you may have skipped over the previous section, so I will repeat the way these data were analyzed because it is crucial to your understanding of the study.
“The unique feature of this study is it compared the health and disability of people who were at the same age when tested but were born in different decades ranging from 1925 to 1955.
Because of the rapid change in diet and lifestyle following World War II, the health and disability of people born in the 1936-1945 decade encompassing World War II was used as the standard to which all other decades were compared.”
When looking at data from the United States, there were two distinct patterns.
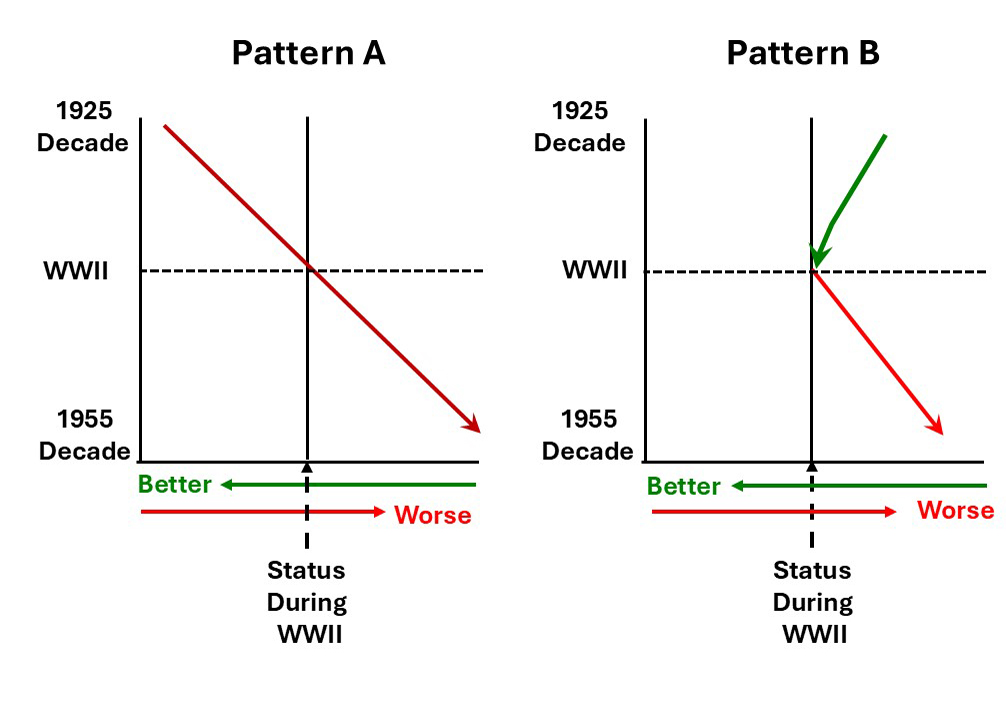 The vertical line in the center of the graph represents the health and disability status of people born during World War II because all comparisons in this study were to people born in the decade encompassing World War II. A worsening of health and disabilities is indicated in red and an improvement in health and disabilities is shown in green.
The vertical line in the center of the graph represents the health and disability status of people born during World War II because all comparisons in this study were to people born in the decade encompassing World War II. A worsening of health and disabilities is indicated in red and an improvement in health and disabilities is shown in green.
Pattern A was characteristic of a constant worsening of health and disabilities from people born in the decade starting in 1925 to people born in the decade starting in 1955.
This pattern was seen for:
- Obesity
- Heart disease.
- Diabetes
- Lung disease.
- High blood pressure.
- High cholesterol.
- Severe disabilities.
- Reduction in grip strength.
Remember, this study is measuring health and disability of people at the same age. The only difference is when they were born. It tells us people in their 50s, 60s, or 70s born in 1955 or later are in poorer health than people of the same age who were born in 1925.
And it’s not just the United States. For obesity and health parameters the pattern was the same for England and Europe. For severe disabilities the pattern was the same for England but was not as clear for Europe.
Two things should be noted for this pattern:
- The worsening of health and the increase in severe disabilities comes despite the vast improvements in the health care systems in these countries and improved understanding of the causes of these diseases.
- Obesity is likely a major driver of our declining health and increased disability. However, it is not the only driver. If the investigators had graphed the percentage of highly processed foods in the diet or the decline in regular exercise, the pattern would have been similar.
Pattern B shows an improvement in the period leading up to World War II and a deterioration in the period after World War II. The authors interpreted the improvement prior to World War II as due to improvements in health care and the deterioration after World War II as due to changes in diet and lifestyle.
This is the pattern seen for mild and moderate disabilities in the United States. The pattern for mild and moderate disabilities was not as clear for England and Europe.
The authors concluded, “In all regions, we found evidence for worsening health across cohorts [groups of people born in successive decades], particularly for those born after 1945.”
What Does This Study Mean For You?
 I don’t want to overinterpret this study. This study breaks new ground, but it has some limitations that I would characterize with three statements:
I don’t want to overinterpret this study. This study breaks new ground, but it has some limitations that I would characterize with three statements:
- It is a very difficult study to do perfectly.
- There are several factors that could affect the interpretation of the data and the outcome of the study.
- The authors made a valiant effort to correct for any factors that could have affected the outcome.
For more details about the factors that might affect the outcome of the study and how the authors corrected for them, read the study.
However, this is the first study to use this approach to gauge the decrease in healthy years (healthspan) in developed countries over the past 40 years. It has its flaws, but it is consistent with several other studies documenting declining health in the current generation of young adults. For example, in a recent issue of “Health Tips From the Professor” I reviewed a study showing that colon cancer rates are increasing at an alarming rate for young adults in this country.
At the beginning of this article, I talked about the gap between our healthspan (how many years we enjoy good health) and our lifespan (how many years we live).
This study suggests that the onset of significant health issues and disabilities is occurring at a younger age today than for people born before World War II. In short, it suggests that our healthspan (the number of healthy years) is getting shorter.
This study did not look at lifespan, but numerous studies show that our lifespan is still increasing. So, the gap between healthspan and lifespan appears to be getting larger. In simple terms this means that when today’s young adults reach their “golden years”, they may spend more of those years in poor health than those of us born in the 1940’s.
But, what does this mean for you? The take home lesson should be, “This doesn’t have to be. You don’t have to be frail and sickly in your golden years. We know how to prevent this.”
- It starts with a healthy diet – a whole food, primarily plant-based diet with lots of colorful fruits and vegetables, whole grains, nuts and seeds.
- Add in a regular exercise program with a mixture of aerobic and resistance exercises.
- Include an individualized supplement program.
You notice I didn’t list weight control as one of the top three prevention strategies. That’s because I don’t recommend fad diets and rapid weight loss programs. If you do the first three things well, your weight will come off naturally – a little bit at a time.
And once you have mastered all four things, you will increase your healthy years and narrow the gap between your healthspan and your lifespan. You can look forward to golden years filled with vitality and adventure.
The Bottom Line
A recent study used an innovative approach to quantify the deterioration in health and the physical ability to function well in daily activities as we age. The unique feature of this study is it compared the health and disability of people who were at the same age when tested but were born in different decades ranging from 1925 to 1955.
The study found a constant worsening of health and disabilities from people born in the decade starting in 1925 to people born in the decade starting in 1955 for:
- Obesity
- Heart disease.
- Diabetes
- Lung disease.
- High blood pressure.
- High cholesterol.
- Severe disabilities.
The authors concluded, “We found evidence for worsening health across cohorts [groups of people born in successive decades], particularly for those born since 1945.”
In short, people born in recent years have fewer healthy years (a shorter healthspan) than people born before World War II. And since our lifespans are getting longer, this means the gap between our healthspan and our lifespan is increasing.
All of us imagine that our golden years will be ones of vibrant health. We’ll travel to exotic places. We’ll take long walks in the mountains. We’ll play with our grandchildren. Life will be wonderful.
But if this study is correct, none of that will happen for many of today’s young adults. They will be too frail and sick to enjoy their golden years.
For more details about this study and how you can increase your healthy years, narrow the gap between your healthspan and your lifespan, and look forward to golden years filled with vitality and adventure, read the article above.
These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This information is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
______________________________________________________________________________
My posts and “Health Tips From the Professor” articles carefully avoid claims about any brand of supplement or manufacturer of supplements. However, I am often asked by representatives of supplement companies if they can share them with their customers.
My answer is, “Yes, as long as you share only the article without any additions or alterations. In particular, you should avoid adding any mention of your company or your company’s products. If you were to do that, you could be making what the FTC and FDA consider a “misleading health claim” that could result in legal action against you and the company you represent.
For more detail about FTC regulations for health claims, see this link.
https://www.ftc.gov/business-guidance/resources/health-products-compliance-guidance
_______________________________________________________________________
About The Author
 Dr. Chaney has a BS in Chemistry from Duke University and a PhD in Biochemistry from UCLA. He is Professor Emeritus from the University of North Carolina where he taught biochemistry and nutrition to medical and dental students for 40 years. Dr. Chaney won numerous teaching awards at UNC, including the Academy of Educators “Excellence in Teaching Lifetime Achievement Award”. Dr Chaney also ran an active cancer research program at UNC and published over 100 scientific articles and reviews in peer-reviewed scientific journals. In addition, he authored two chapters on nutrition in one of the leading biochemistry text books for medical students.
Dr. Chaney has a BS in Chemistry from Duke University and a PhD in Biochemistry from UCLA. He is Professor Emeritus from the University of North Carolina where he taught biochemistry and nutrition to medical and dental students for 40 years. Dr. Chaney won numerous teaching awards at UNC, including the Academy of Educators “Excellence in Teaching Lifetime Achievement Award”. Dr Chaney also ran an active cancer research program at UNC and published over 100 scientific articles and reviews in peer-reviewed scientific journals. In addition, he authored two chapters on nutrition in one of the leading biochemistry text books for medical students.
Since retiring from the University of North Carolina, he has been writing a weekly health blog called “Health Tips From the Professor”. He has also written two best-selling books, “Slaying the Food Myths” and “Slaying the Supplement Myths”. And most recently he has created an online lifestyle change course, “Create Your Personal Health Zone”. For more information visit https://chaneyhealth.com.
For the past 45 years Dr. Chaney and his wife Suzanne have been helping people improve their health holistically through a combination of good diet, exercise, weight control and appropriate supplementation.