Can DHA Help Johnny Read?
Author: Dr. Stephen Chaney
 If you are like most parents, you want to do everything you can to assure that your kids have the skills they need to succeed in school, and reading probably tops the list of necessary skills. If your child is reading below their age level, could something as simple as better nutrition improve their reading ability?
If you are like most parents, you want to do everything you can to assure that your kids have the skills they need to succeed in school, and reading probably tops the list of necessary skills. If your child is reading below their age level, could something as simple as better nutrition improve their reading ability?
Recent studies have shown that the omega-3 fatty acids, especially DHA, play a very important role in normal brain function – especially memory, focus, concentration, and attention span.
I have shared with you previous studies which have shown that optimal DHA intake in pregnant women plays an important role in the early mental development of their children. On the other end of the age spectrum, studies have shown that optimal omega-3 fatty acid intake in older adults can delay cognitive decline.
I have also shared with you studies showing that omega-3 fatty acid supplementation in children with ADD and ADHD significantly reduce their symptoms. What about children without hyperactivity? Could omega-3 fatty acids affect their ability to learn?
Many Children Are Deficient in Omega-3 Fatty Acids
The Food and Nutrition Board has not yet set US standards for DHA intake, but the international standard is 200 mg for children 7 years old and older. Unfortunately, cod liver oil is a thing of the past, and foods rich in DHA are not particularly popular with children. Consequently, most children in this country are only getting around 20-40 mg of DHA per day.
And that shows up in their blood levels of omega-3 fatty acids. A recent study in England looked at blood levels of omega-3 fatty acids in 493 seven to nine year olds with below average reading performance who were enrolled in Oxfordshire primary schools (P. Montgomery et al, PLoS ONE, doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066697).
All of them had low blood levels of omega-3 fatty acids (both DHA and EPA), and the blood levels of omega-3 fatty acids were directly related to their reading ability. In non-scientific language that simply means that those with the poorest reading abilities had the lowest blood levels of omega-3 fatty acids.
This study is particularly significant because another study by the same group showing that DHA supplementation improved reading skills in underperforming children.
Could Omega-3s Improve Reading Skills?
This study (Richardson et al., PLoS ONE 7: e43909.doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0043909) looked at 362 normal 7-9 year old children enrolled in mainstream primary schools in Oxfordshire, England.
These children were all reading at significantly below the average for their grade levels. The study excluded children with specific medical difficulties that might affect their ability to read, children who were already taking medications expected to affect behavior or learning, children for whom English was not their first language, and children who were already eating fish more than twice a week or taking omega-3 supplements.
The children were given either supplements containing 600 mg of DHA per day or a placebo containing corn and soybean oil. At the end of 16 weeks the children were rescored on a standardized reading test.
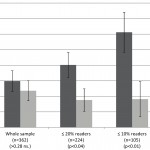 The results were quite interesting. When the scientists looked at children reading in the lower third of their class, the affect of DHA on their ability to read was non-significant. However, when they looked at the children who were performing in the bottom 20% of their class with respect to reading, DHA supplementation resulted in a 20% improvement in their reading score. And when they looked at children in the bottom 10% of their class with respect to reading, DHA supplementation resulted in a 50% increase in reading scores. These changes were highly significant.
The results were quite interesting. When the scientists looked at children reading in the lower third of their class, the affect of DHA on their ability to read was non-significant. However, when they looked at the children who were performing in the bottom 20% of their class with respect to reading, DHA supplementation resulted in a 20% improvement in their reading score. And when they looked at children in the bottom 10% of their class with respect to reading, DHA supplementation resulted in a 50% increase in reading scores. These changes were highly significant.
To put this in perspective, the children performing in the bottom 20% of their class improved their reading efficiency by around 0.8 months with respect to their normal reading age, and the children in the bottom 10% of their class improved their reading efficiency by around 1.9 months with respect to their normal reading age.
Strengths and Weaknesses of The Studies
On The Minus Side:
- First and foremost we must remember that nutrition is only one of many factors that can affect reading performance in children. You shouldn’t think of DHA as a magic bullet that will cure your child’s reading problems by itself.
- This is a single pair of studies that need to be replicated.
- This study does not establish the optimal dose of DHA needed to improve reading in underperforming children. Until dose response studies have been done we don’t know whether 600 mg is needed or whether simply making sure that the children reach the recommended 200 mg per day of DHA would be sufficient.
On The Plus Side:
- Both of these were very well controlled studies, and they complemented each other perfectly. One study showed that students with the poorest reading ability had the lowest blood levels of DHA. The other study showed that children with the poorest reading ability experienced the greatest improvement with DHA supplementation.
- These studies were not done with third world children. They were studies with normal, healthy children in a prosperous European country.
- These studies are fully consistent with previous studies looking at the effects of DHA on cognition in children.
The Bottom Line
What does this study mean for parents whose children may be struggling with their reading in school?
- The lead author concluded: “We have shown that in the mainstream, general population, something as simple as DHA can benefit reading abilities in underperforming children.”
- It’s perhaps not that ironclad yet. But if your kid or grandkid is reading below their grade level, DHA supplementation is both safe and inexpensive. It’s worth giving it a try.
These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This information is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any disease.