Is Fructose Bad For You?
Author: Dr. Stephen Chaney
 I don’t usually report on studies done in mice, but this study sheds light on a particularly puzzling question: Why is fructose bad for us?
I don’t usually report on studies done in mice, but this study sheds light on a particularly puzzling question: Why is fructose bad for us?
The studies are clear-cut. High fructose consumption is associated with inflammation, obesity, non-alcoholic liver disease, insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, kidney disease, increased LDL cholesterol and triglycerides, and heart disease. Based on these associations, fructose appears to be deadly. Why would anyone want to consume it?
Yet fructose is found in virtually every fruit. In fact, fructose, also known as fruit sugar, was first isolated from fruits. Hence the name fructose. Humans have been eating fruits safely for thousands of years. Fruits are very good for us. That raises the question: “If fruits are good for us, how can fructose be bad for us?”.
An important clue can be found by looking at what the food industry has done to the American diet. Because fructose imparts a pleasurable, sweet taste to foods the food industry keeps adding it to more and more foods. As a result, dietary intake of fructose has increased 100-fold over the past two centuries. It has reached the point where fructose now accounts for almost 10% of the caloric intake in the United States.
Is It The Sugar, Or Is It The Food?
Let me expand the discussion by using a couple of graphics I developed for my book, “Slaying The Food Myths”
There Are No Sugar Villains. There Are No Sugar Heroes:
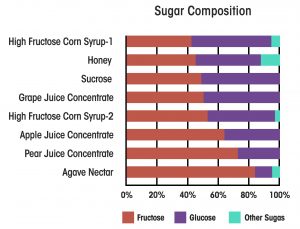 Virtually all sweeteners are primarily a mixture of fructose and glucose. The graphic on the left compares high fructose corn syrup (the current villain) with other “natural” sweeteners used in foods (our current heroes). High fructose corn syrup ranges from about 40% fructose to 55% fructose. The exact percentage depends on what kind of food product is being made with it.
Virtually all sweeteners are primarily a mixture of fructose and glucose. The graphic on the left compares high fructose corn syrup (the current villain) with other “natural” sweeteners used in foods (our current heroes). High fructose corn syrup ranges from about 40% fructose to 55% fructose. The exact percentage depends on what kind of food product is being made with it.
Honey and coconut sugar are about 45% fructose. Sucrose and grape juice concentrate are around 50% fructose. Apple juice concentrate is around 60% fructose, and agave sugar comes in at a whopping 80% fructose.
In other words, if fructose is the culprit that everyone makes it out to be, “healthy” sugars are no better than high fructose corn syrup. Simply substituting a “healthy” sugar for high fructose corn syrup is unlikely to provide any meaningful benefit.
Is It The Sugar, Or Is The Food?
 This graphic shows us what a nutrition label would look like on a medium apple. I am sure that label is a wake-up call for many of you. The amount of sugar and the percentage of fructose and glucose are about the same as in an 8-ounce soda sweetened with high fructose corn syrup. The same is true for virtually every other fruit you can think of.
This graphic shows us what a nutrition label would look like on a medium apple. I am sure that label is a wake-up call for many of you. The amount of sugar and the percentage of fructose and glucose are about the same as in an 8-ounce soda sweetened with high fructose corn syrup. The same is true for virtually every other fruit you can think of.
Now let me share one more thing you won’t hear from what I refer to as “Dr. Strangelove’s Health Blog” (You probably know the ones I am referring to). Virtually all the studies showing the bad effects of fructose consumption have been done with sodas and sugary junk foods. They haven’t been done with apples.
In fact, virtually every study looking at fruit and vegetable consumption has shown they are incredibly good for us. They lower inflammation and reduce the risk of obesity, diabetes, heart disease, and cancer. And the more the better. One study found that the health benefits of fruit and vegetable consumption topped out at around 10 servings a day.
With this background, you should now fully understand why the question “If fruits are good for us, how can fructose be bad for us?” is so perplexing.
My simplistic explanation has always been that whole foods like fruits have fiber, which slows the absorption of fructose from the intestine. Our bodies were designed to handle fructose in a safe manner when it enters the bloodstream slowly. It is taken up by the liver, converted to glucose, and then slowly metered back into the bloodstream. This provides our brain and other tissues with the glucose they need for energy without blood sugar spikes. This is how fructose is supposed to be metabolized by our bodies.
Sodas and junk foods, on the other hand, have little to slow the absorption of fructose. When lots of fructose enters the bloodstream rapidly, our “safe” metabolic pathways for handling it are overwhelmed, and it is forced into the pathways that are harmful. For example, the “excess” fructose is converted to fat by the liver, which causes inflammation, obesity, fatty liver disease, and triglyceride production.
This is, of course, simply my hypothesis for explaining the different effect of fructose in fruits and sodas. It is based on sound metabolic principles, but it is far from proven. That is why I found a recent study (C. Jang et al, Cell Metabolism, 27: 351-361, 2018) so interesting. It provides a metabolic rationale for my hypothesis.
How Was The Study Done?
Mice were fed a 1:1 mixture of fructose and glucose at doses that approximated the ranges of typical human fructose consumption. The fructose was isotopically labeled so that fructose and its metabolites could be identified by LC-MS (liquid chromatography – mass spectrometry). After feeding the mice the labeled fructose, the investigator measured the amount of fructose and its metabolites in various organs and in the portal vein, which transports sugars from the intestine to the liver for additional metabolism before they enter the bloodstream.
Is Fructose Bad For You?
 The first surprise was that most of the fructose was metabolized by the intestinal mucosal cells that line the small intestine rather than the liver. Previous reports had assumed that fructose was primarily metabolized by the liver because that was where most of the bad effects of fructose metabolism had been observed.
The first surprise was that most of the fructose was metabolized by the intestinal mucosal cells that line the small intestine rather than the liver. Previous reports had assumed that fructose was primarily metabolized by the liver because that was where most of the bad effects of fructose metabolism had been observed.
These investigators observed that fructose was primarily converted to glucose and small molecular weight metabolites by the intestinal mucosal cells before being released into the portal vein, where they were transported to the liver. However, there was a strong dose response effect.
- At low fructose doses, 90% of fructose was metabolized by intestinal mucosal cells before being released to the liver.
- At high fructose doses, only 70% of fructose was metabolized by intestinal mucosal cells.
- That means at high fructose doses the amount of fructose reaching the liver unchanged increases from 10% to 30%. That is a 3-fold increase!
The authors concluded:
- “Based on these findings, we propose that the small intestine shields the liver from fructose and that excessive doses of fructose overwhelm the small intestine, spilling over to the liver where they cause toxicity.”
- “A key difference between the health effects of fiber-rich fruits (and perhaps even fiber-rich prepared foods) and juices/sodas is their rate of intestinal fructose release.”
- “It is likely that the appearance rate of free fructose in the small intestine plays a critical role in dictating its metabolic fate. Like the lower doses in our experiments, a slower rate of fructose appearance will result in more complete intestinal clearance, whereas higher doses and faster rates result in fructose overflow to the liver.”
This study needs to be confirmed, and the mechanism may be entirely different in humans. However, whether mechanism is the same in mice and humans is immaterial. We already know that fructose in sodas and junk foods exerts a very different effect on our health than fructose in fruits and other fiber-containing foods.
Despite what Dr. Strangelove tells you, fructose is not bad for you. It isn’t the problem. It is sodas and junk foods containing high-fructose corn syrup that are the problem. And substituting other sugars for high-fructose corn syrup doesn’t make them any better. As I showed you above, the so called “healthy” sugars are chemically and biologically indistinguishable from high-fructose corn syrup.
The Bottom Line
Previous studies have clearly shown that fructose in sodas and junk foods is bad for us, while fructose in fruits is good for us. A recent study in mice provides a metabolic explanation for this difference. The study found:
- At low fructose doses, 90% of fructose was metabolized by intestinal mucosal cells before being released to the liver.
- At high fructose doses, only 70% of fructose was metabolized by intestinal mucosal cells.
- That means at high fructose doses the amount of fructose reaching the liver unchanged increases from 10% to 30%. That is a 3-fold increase!
The authors concluded:
- “Based on these findings, we propose that the small intestine shields the liver from fructose and that excessive doses of fructose overwhelm the small intestine, spilling over to the liver where they cause toxicity.”
- “A key difference between the health effects of fiber-rich fruits (and perhaps even fiber-rich prepared foods) and juices/sodas is their rate of intestinal fructose release.”
- “It is likely that the appearance rate of free fructose in the small intestine plays a critical role in dictating its metabolic fate. Like the lower doses in our experiments, a slower rate of fructose appearance will result in more complete intestinal clearance, whereas higher doses and faster rates result in fructose overflow to the liver.”
This study needs to be confirmed, and the mechanism may be entirely different in humans. However, whether mechanism is the same in mice and humans is immaterial. We already know that fructose in sodas and junk foods exerts a very different effect on our health than fructose in fruits and other fiber-containing foods.
Despite what Dr. Strangelove tells you, fructose is not bad for you. It isn’t the problem. It is sodas and junk foods containing high-fructose corn syrup that are the problem. And substituting other sugars for high-fructose corn syrup doesn’t make them any better. As I showed you above, the so called “healthy” sugars are chemically and biologically indistinguishable from high-fructose corn syrup.
For more details, read the article above.
These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This information is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
