What Is Nutritionism?
 Recently, I have been reading Michael Pollan’s book “In Defense of Food”. Yes, I know the book has been around for a long time. Normally I read the scientific literature rather than popular health books. However, in the past few weeks I have had a lot more time to read books, so I decided to read this one.
Recently, I have been reading Michael Pollan’s book “In Defense of Food”. Yes, I know the book has been around for a long time. Normally I read the scientific literature rather than popular health books. However, in the past few weeks I have had a lot more time to read books, so I decided to read this one.
Some of the things he says are “off the wall”. As he readily admits, he isn’t a scientist or a medical doctor. However, a lot of what he says is “right on”. He echoes many of the things I have been talking about for years. But he does a masterful job of pulling everything together into a framework he calls “nutritionism”.
If you have a chance, I highly recommend that you read his book.
I will briefly summarize his discussion of nutritionism below. I will also share some scientific support for what he is saying. Finally, I will close by sharing what the Bible says on the subject.
What Is Nutritionism?
 Simply put, nutritionism is the belief that we can understand food solely in terms of its nutritional and chemical constituents and our requirements for them. I use the term “belief” purposely. As Michael Pollan puts it: “As the ‘-ism’ suggests, nutritionism is not a scientific subject, but an ideology.”
Simply put, nutritionism is the belief that we can understand food solely in terms of its nutritional and chemical constituents and our requirements for them. I use the term “belief” purposely. As Michael Pollan puts it: “As the ‘-ism’ suggests, nutritionism is not a scientific subject, but an ideology.”
What Michael Pollan is referring to is taking food constituents like saturated fats, cholesterol, sugar, carbohydrates, polyunsaturated fats, monounsaturated fats, fiber, antioxidants, and probiotics and labeling them as either “good” or “bad”.
As he points out, that leads to debacles like the creation of margarine as a substitute for butter. Of course, everyone reading this article knows that we subsequently found out that the trans fat in margarine was worse for us than the saturated fat in butter. He offers many other examples like this.
He also points out that the nutritionism concept has given free rein to the food industry to replace whole foods with processed foods that are cholesterol-free, sugar-free, low-fat, low-carb, or high in fiber, omega-3s, etc. He says that these foods are seldom healthier than the foods they replace. I agree.
Finally, he points out that the scientific support for the classification of individual ingredients or foods as “good” or “bad” is weak. That’s because when scientists design a study that removes a chemical constituent or a food from the diet, they have to replace it with something. And what they replace it with determines the outcome of the study. I give some examples of this in the next section.
The essence of Michael Pollan’s message is:
- The effect of an individual nutrient or chemical constituent on your health depends on the food it is found in. Forget the fancy nutrition labels. Whole foods are almost always healthier than processed foods.
- The effect of a food or food constituent on your health also depends on your overall diet. We should be thinking about healthy diets rather than the latest “magical” or “forbidden” food.
I will discuss these points below.
Which Foods Should I Avoid?
 Now, let’s get to the question, “Which Foods Should I Avoid?” If we are talking about whole foods, the short answer is “None”. As I said in my book, “Slaying The Food Myths”, “We have 5 food groups for a reason”.
Now, let’s get to the question, “Which Foods Should I Avoid?” If we are talking about whole foods, the short answer is “None”. As I said in my book, “Slaying The Food Myths”, “We have 5 food groups for a reason”.
For example, if we are talking about plant foods, each plant food group:
- Has a unique blend of vitamins and minerals.
- Has a unique blend of phytonutrients.
- Has a unique blend of fiber.
- Supports the growth of a unique combination of beneficial gut bacteria.
- Dr Strangelove and his friends are telling you to eliminate whole grains, fruits, and legumes (beans) from your diet. Recent studies suggest that might not be a good idea. Here is one example.
If we are talking about animal foods, each animal food group:
- Has a unique blend of vitamins and minerals.
- May have unique components that are important for our health. [Note: This is an active area of research. Theories have been proposed for which components in animal foods may be important for our health, but they have not been confirmed.]
- Vegan purists will tell you that you have no need for meat and dairy foods. Recent studies suggest otherwise. Here is one example.
With that as background, let’s turn our attention to nutritionism and look at some of science behind claims that certain food components are either good for us or bad for us.
Saturated Fat. Saturated fat is the poster child for nutritionism.
First, we were told by the American Heart Association and other health organizations that saturated fat was bad for us. Recently Dr. Strangelove and his friends are telling us that saturated fat is good for us. Instead of limiting saturated fat, we should be limiting carbs by cutting out fruits, whole grains, and legumes. Both cite clinical studies to support their claims. How can this be?
Perhaps a little history is in order. When the American Heart Association recommended that we decrease intake of saturated fat, they were envisioning that we would replace it with monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fat in the context of a healthy diet of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes. That never happened.
Big Food quickly realized that if the American public were to follow the AHA guidelines, it would be disastrous for their bottom line. So, they sprang into action. They mixed sugar, white flour, and a witch’s brew of chemicals to create highly processed, low fat “foods”. Then they told the American public, “Don’t worry. You don’t have to give up your favorite foods. We have created low fat alternatives.”
This is the essence of what Michael Pollan refers to as nutritionism. By marketing their fake foods as low fat Big Food created the halo of health. In fact, Big Food’s fake foods were less healthy than the foods they replaced. Americans got fatter and sicker.
Now let’s look at the conflicting claims that saturated fat is bad for us or good for us. How can clinical studies disagree on such an important question? The answer is simple. It depends on what you replace it with. You need to consider saturated fat intake in the context of the overall diet.
I discussed this in a previous issue of “Health Tips From the Professor”, but let me summarize it briefly here. The American Heart Association tells us that replacing half of the saturated fat in a typical American diet with:
- Trans fats, increases heart disease risk by 5%.
- Refined carbohydrates and sugars (the kind of carbohydrates in the typical American Diet), slightly increases heart disease risk.
- Complex carbohydrates (whole grains, fruits & vegetables), decreases heart disease risk by 9%.
- Monounsaturated fats (olive oil & peanut oil), decreases heart disease risk by 15%.
- Polyunsaturated fats (vegetable oils and fish oil), decreases heart disease risk by 25%.
- Unsaturated fats in the context of a Mediterranean diet, decreases heart disease risk by 45%.
My advice: Saturated fat is neither good for you nor bad for you. A little bit of saturated fat in the context of a healthy diet is fine. A lot of saturated fat in the context of an unhealthy diet is problematic.
 Red Meat. Is red meat bad for you? Like saturated fat, it depends on the amount of red meat and the overall diet. I covered this in detail in “Slaying The Food Myths”, but let me summarize briefly here:
Red Meat. Is red meat bad for you? Like saturated fat, it depends on the amount of red meat and the overall diet. I covered this in detail in “Slaying The Food Myths”, but let me summarize briefly here:
According to the World Health Organization, red meat is a probable carcinogen. If we look at the postulated mechanisms by which it causes cancer, they can be mostly neutralized by components of various plant foods.
My advice: An 8-ounce steak with fries and a soda is probably bad for you. Three ounces of that same steak in a green salad or stir fry may be good for you.
I should make one other point while I am on the topic. Dr. Strangelove and his friends have been telling you that grass-fed beef is better for you than conventionally raised beef. Once again, that is nutritionism. Grass-fed beef is lower in saturated fat and high in omega-3s than conventionally raised beef. That may be better for your heart, but it has no effect on the cancer-causing potential of red meat. It doesn’t give the license to eat 8-ounce steaks on a regular basis. You still want to aim for 3-ounces of that grass-fed beef in a green salad or stir fry.
High-Fructose Corn Syrup. This one seems to be on everyone’s “naughty list”. You are being told to read labels, and if the food has high-fructose corn syrup on the label, put it back on the shelf. But is that good advice?
It turns out that all the studies on the bad effects of high-fructose corn syrup have been done with sodas and highly processed foods. This should be your first clue.
Of course, as soon as high-fructose corn syrup gained its “bad” reputation, Big Food started replacing it with 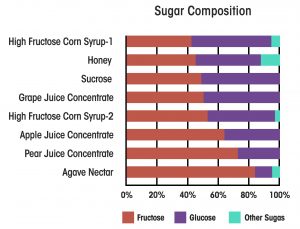 “heathier” sugars. Does that make those foods healthier?
“heathier” sugars. Does that make those foods healthier?
The answer is a clear “No”. Both chemically and biologically, high-fructose corn syrup is identical to sucrose (table sugar), honey, molasses, maple syrup, coconut sugar, date sugar, or grape juice concentrate. Agave sugar is even higher in fructose than high-fructose corn syrup. This is your second clue.
Substituting these sugars for high-fructose corn syrup doesn’t turn sodas and processed foods into health foods. This is nutritionism at its worst.
My advice: Forget reading the label. Forget trying to avoid foods with high-fructose corn syrup. Avoid sodas and processed foods instead.
Sugar. Once the public started to realize that natural sugars in processed foods were just as bad for us as high-fructose corn syrup, sugars became “bad”. We were told to avoid all foods containing sugar in any form. In fact, we were told we needed to become “label detectives” and recognize all the deceptive ways that sugar could be hidden on the label.
 I have discussed this in detail in a previous issue of “Health Tips From The Professor”.
I have discussed this in detail in a previous issue of “Health Tips From The Professor”.
Let me just summarize that article with one quote, “It’s not the sugar. It’s the food. There is the same amount and same types of sugar in an 8-ounce soda and a medium apple. Sodas are bad for you, and apples are good for you.” If you are wondering why that is, I have covered it in another issue of “Health Tips From the Professor”.
Before leaving this subject, I should mention that nutritionism has risen its ugly head here as well. Big Food has struck again. They have replaced sugar with a variety of artificial sweeteners.
Once again, nutritionism has failed. Those artificially sweetened sodas and processed foods are no healthier and no more likely to help you keep the weight off than the sugar-sweetened foods they replace. I have covered the science behind that statement in several previous issues of “Health Tips From the Professor”. Here is one example.
My advice: Forget about sugar phobia. You don’t need to become a label detective. Just avoid sodas, sugar-sweetened beverages, and sweet processed foods. Get your sugar in its natural form in fruits and other whole foods.
 Carbs. Dr. Strangelove and his friends are now telling you that you need to avoid all carbs. That is pure nutritionism. Carbs are neither good nor bad. It depends on the type of carb and what you replace it with.
Carbs. Dr. Strangelove and his friends are now telling you that you need to avoid all carbs. That is pure nutritionism. Carbs are neither good nor bad. It depends on the type of carb and what you replace it with.
Once again, clinical studies have given conflicting outcomes. Each side of the carbohydrate debate can provide clinical studies to support their position. How can that be? The answer is simple. It depends on what assumptions went into the design of the clinical studies. I have written several articles on this topic in “Health Tips From the Professor”, but let me give you one example here.
In this example, I looked at two major studies. The PURE (Prospective Urban Rural Epidemiology) study included data from 135,000 participants in 18 countries. In this study, the death rate decreased as the % carbohydrate in the diet decreased. The low-carb enthusiasts were doing a victory dance.
However, it was followed by a second, even larger study. The ARIC (Atherosclerosis Risk In Communities) study included 432,000 participants from even more countries. In this study, the death rate decreased as the % carbohydrate decreased to about 40%. Then a curious thing happened. As the % carbohydrate in the diet decreased further, the death rate increased.
How can you explain this discrepancy? When you examine the PURE study:
- The % carbohydrate only ranged from 70% to 40%.
- The data for the PURE study was obtained primarily with third world countries. That is an important distinction because:
-
- In those countries, it is primarily the well to do that can afford sodas, processed foods, and meat.
-
- The poor subsist on what they can grow and inexpensive staples like beans and rice.
- Simply put, in the PURE study, the type of carbohydrate changed as well as the amount of carbohydrate.
-
- At the highest carbohydrate intakes, a significant percentage of the carbohydrate came from sugar and refined grains.
-
- At the lowest carbohydrate intakes, most of the carbohydrate intake came from beans, whole grains, and whatever fruits and vegetables they could grow.
When you examine the ARIC study: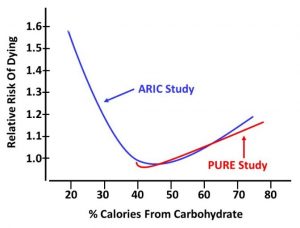
- The % carbohydrate ranged from 70% to 20%.
- The ARIC study added in data from the US and European countries. That is an important distinction because:
-
- Low carb diets like Atkins and Keto are popular in these countries. And those are the diets that fall into the 20-40% carbohydrate range.
-
- Most people can afford diets that contain a lot of meat in those countries.
- Simply put, at the lower end of the scale in the ARIC study, people were eating diets rich in meats and saturated fats and eliminating healthy carbohydrate-containing foods like fruits, whole grains and legumes.
My advice: The lesson here is to avoid simplistic nutritionism thinking and focus on diets rather than on foods. When you do that it is clear that carbs aren’t bad for you, it’s unhealthy carbs that are bad for you.
Which Foods Should I Avoid? By now the answer to the question, “Which Foods Should I Avoid?” is clear. Avoid sodas, sugar-sweetened beverages and processed foods (The term processed foods includes convenience foods, junk foods, and most sweets).
What Does This Mean To You?
 Now that we are clear on which foods you should avoid, let’s look at the flip side of the coin. Let’s ask, “Which foods should you include in your diet?
Now that we are clear on which foods you should avoid, let’s look at the flip side of the coin. Let’s ask, “Which foods should you include in your diet?
As I said at the beginning of this article, “We have 5 food groups for a reason”. We should consider whole foods from all 5 food groups as healthy.
Of course, each of us is different. We all have foods in some food groups that don’t treat us well. Some of us do better with saturated fats or carbs than others. We need to explore and find the foods and diets that work best for us.
However, whenever we assume one diet is best for everyone, we have crossed the line into nutritionism.
What Does The Bible Say?
Let me start this section by saying that I rely on the Bible for spiritual guidance rather than nutritional guidance. However, as part of our church’s Bible reading plan, I was reading 1 Timothy. A passage from 1 Timothy 4:1-5 leapt out at me. It reinforces the theme of Michael Pollan’s book and seems uniquely applicable to the times we live in.
“The Spirit clearly says that in later times some will abandon the faith and follow deceiving spirits and things taught by demons. Such teachings come through hypocritical liars, whose consciences have been seared as with a hot iron. They…order people to abstain from certain foods, which God created to be received with thanksgiving by those who believe and who know the truth. For everything God created is good, and nothing is to be rejected if it is received with thanksgiving, because it is consecrated by the word of God and prayer.”
Interesting.
The Bottom Line
In this article, I have discussed the concept of “nutritionism” introduced in Michael Pollan’s book “In Defense Of Food”. He defines nutritionism as the belief that we can understand food solely in terms of its nutritional and chemical constituents and our requirements for them.
What Michael Pollan is referring to is taking food constituents like saturated fats, cholesterol, sugar, carbohydrates, polyunsaturated fats, monounsaturated fats, fiber, antioxidants, and probiotics and labeling them as either “good” or “bad”. He points out that when we accept these simplistic labels, we often end up creating foods and diets that are less healthy than the ones we were trying to replace.
At the beginning of the article, I asked the question, “Which Foods Should I Avoid?” I then looked at several foods or food groups we have told to avoid, including saturated fats, red meat, high-fructose corn syrup, sugar, and carbs. When you look at the science behind these recommendations from the lens of nutritionism, you come to two conclusions:
- We should avoid sodas, sugar-sweetened beverages and processed foods (The term processed foods includes convenience foods, junk foods, and most sweets).
- Whole foods from all 5 food groups should be considered as healthy.
Of course, each of us is different. We all have foods in some food groups that don’t treat us well. Some of us do better with saturated fats or carbs than others. We need to explore and find the foods and diets that work best for us.
However, whenever we assume one diet is best for everyone, we have crossed the line into nutritionism.
For more details and a bible verse that supports the theme of Michael Pollan’s book and seems uniquely applicable to the times we live in, read the article above.
These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This information is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
 It seems like just yesterday that health experts all agreed that whole grains were good for us. After all:
It seems like just yesterday that health experts all agreed that whole grains were good for us. After all: Dr. Strangelove and his colleagues are claiming that whole grains cause inflammation, which increases your risk of heart disease and cancer. Heart disease and cancer are the leading causes of death in this country. In fact, according to the CDC, heart disease and cancer accounted for 44% of all deaths in the US in 2017.
Dr. Strangelove and his colleagues are claiming that whole grains cause inflammation, which increases your risk of heart disease and cancer. Heart disease and cancer are the leading causes of death in this country. In fact, according to the CDC, heart disease and cancer accounted for 44% of all deaths in the US in 2017. whole grains people consumed, the lower the risk of deaths from heart disease, cancer, and all causes.
whole grains people consumed, the lower the risk of deaths from heart disease, cancer, and all causes. As for the original question, “Should I avoid whole grains?”, the answer appears to be a clear, “No”.
As for the original question, “Should I avoid whole grains?”, the answer appears to be a clear, “No”.