Supplements Are Part of a Holistic Lifestyle
Author: Dr. Stephen Chaney
 The headlines about supplementation are so confusing. Are they useful, or are they a waste of money? Will they cure you, or will they kill you? I feel your pain.
The headlines about supplementation are so confusing. Are they useful, or are they a waste of money? Will they cure you, or will they kill you? I feel your pain.
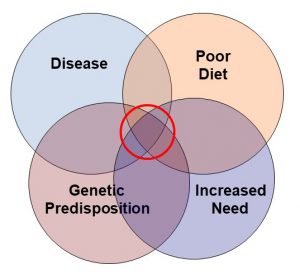
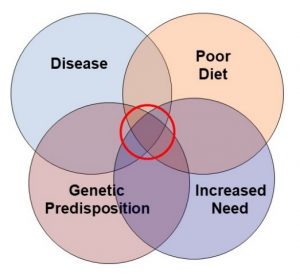
I have covered these questions in depth in my book, “Slaying The Supplement Myths”, but let me give you a quick overview today. I call it: “Who Benefits Most From Supplementation?” I created the graphic on the left to illustrate why I feel responsible supplementation is an important part of a holistic lifestyle for most Americans. Let me give you specific examples for each of these categories.
Examples of Poor Diet
 You have heard the saying that supplementation fills in the nutritional gaps in our diets, so what are the nutritional gaps? According to the USDA’s 2020-2025 Dietary Guidelines for Americans, many Americans are consuming too much fast and convenience foods. Consequently, we are getting inadequate amounts of calcium, magnesium, and vitamins A, D, E and C. Iron is considered a nutrient of concern for young children and pregnant women. In addition, folic acid, vitamin B6, and iodine are nutrients of concern for adolescent girls and pregnant women.
You have heard the saying that supplementation fills in the nutritional gaps in our diets, so what are the nutritional gaps? According to the USDA’s 2020-2025 Dietary Guidelines for Americans, many Americans are consuming too much fast and convenience foods. Consequently, we are getting inadequate amounts of calcium, magnesium, and vitamins A, D, E and C. Iron is considered a nutrient of concern for young children and pregnant women. In addition, folic acid, vitamin B6, and iodine are nutrients of concern for adolescent girls and pregnant women.
According to a recent study, regular use of a multivitamin is sufficient to eliminate all these deficiencies except for calcium, magnesium and vitamin D (J.B. Blumberg et al, Nutrients, 9(8): doi: 10.3390/nu9080849, 2017). A well-designed calcium, magnesium and vitamin D supplement may be needed to eliminate those deficiencies.
In addition, intake of omega-3 fatty acids from foods appears to be inadequate in this country. Recent studies have found that American’s blood levels of omega-3s are among the lowest in the world and only half of the recommended level for reducing the risk of heart disease (K.D. Stark et al, Progress In Lipid Research, 63: 132-152, 2016; S.V. Thuppal et al, Nutrients, 9, 930, 2017; M Thompson et al, Nutrients, 11: 177, 2019). Therefore, omega-3 supplementation is often a good idea.
In previous editions of “Health Tips From the Professor” I have talked about our “mighty microbiome”, the bacteria and other microorganisms in our intestine. These intestinal bacteria can affect our tendency to gain weight, our immune system, inflammatory diseases, chronic diseases such as diabetes, cancer, and heart diseases, our mood—the list goes on and on. This is an emerging science. We are learning more every day, but for now it appears our best chances for creating a health-enhancing microbiome are to consume a primarily plant-based diet and take a probiotic supplement.
Finally, diets that eliminate whole food groups create nutritional deficiencies. For example, vegan diets increase the risk of deficiencies in vitamin B12, vitamin D, calcium, iron, zinc and long chain omega-3 fatty acids. A recent study reported that the Paleo diet increased the risk of calcium, magnesium, iodine, thiamin, riboflavin, folate and vitamin D deficiency (A. Genomi et al, Nutrients, 8, 314, 2016). The Keto diet is even more restrictive and is likely to create additional deficiencies.
Examples of Increased Need
 We have known for years that pregnancy and lactation increase nutritional requirements. In addition, seniors have increased needs for protein, calcium, vitamin D and vitamin B12. In previous issues of “Health Tips From the Professor” I have also shared recent studies showing that protein requirements are increased with exercise.
We have known for years that pregnancy and lactation increase nutritional requirements. In addition, seniors have increased needs for protein, calcium, vitamin D and vitamin B12. In previous issues of “Health Tips From the Professor” I have also shared recent studies showing that protein requirements are increased with exercise.
Common medications also increase our need for specific nutrients. For example, seizure medications can increase your need for vitamin D and calcium. Drugs to treat diabetes and acid reflux can increase your need for vitamin B12. Other drugs increase your need for vitamin B6, folic acid, and vitamin K. Excess alcohol consumption increases your need for thiamin, folic acid, and vitamin B6. These are just a few examples.
Vitamin D is a special case. Many people with apparently adequate intake of vitamin D have low blood levels of 25-hydroxy vitamin D. It is a good idea to have your blood 25-hydroxy vitamin D levels measured on an annual basis and supplement with vitamin D if they are low.
More worrisome is the fact that we live in an increasing polluted world and some of these pollutants may increase our needs for certain nutrients. For example, in a recent edition of “Health Tips From the Professor” I shared a study reporting that exposure to pesticides during pregnancy increases the risk of giving birth to children who will develop autism, and that supplementation with folic acid during pregnancy reduces the effect of pesticides on autism risk. I do wish to acknowledge that this is a developing area of research. This and similar studies require confirmation. It is, however, a reminder that there may be factors beyond our control that have the potential to increase our nutritional needs.
Examples of Genetics Influencing Nutritional Needs
 The effect of genetic variation on nutritional needs is known as nutrigenomics. One of the best-known examples of nutrigenomics is genetic variation in the methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) gene. MTHFR gene mutations increase the risk of certain birth defects, such as neural tube defects. MTHFR mutations also slightly increase the requirement for folic acid. A combination of food fortification and supplementation with folic acid have substantially decreased the prevalence of neural tube defects in the US population. This is one of the great success stories of nutrigenomics. Parenthetically, there is no evidence that methylfolate is needed to decrease the risk of neural tube defects in women with MTHFR mutations.
The effect of genetic variation on nutritional needs is known as nutrigenomics. One of the best-known examples of nutrigenomics is genetic variation in the methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) gene. MTHFR gene mutations increase the risk of certain birth defects, such as neural tube defects. MTHFR mutations also slightly increase the requirement for folic acid. A combination of food fortification and supplementation with folic acid have substantially decreased the prevalence of neural tube defects in the US population. This is one of the great success stories of nutrigenomics. Parenthetically, there is no evidence that methylfolate is needed to decrease the risk of neural tube defects in women with MTHFR mutations.
Let me give you a couple of additional examples:
One of them has to do with vitamin E and heart disease (A.P. Levy et al, Diabetes Care, 27: 2767, 2004). Like a lot of other studies there was no significant effect of vitamin E on cardiovascular risk in the general population. But there is a genetic variation in the haptoglobin gene that influences cardiovascular risk. The haptoglobin 2-2 genotype increases oxidative damage to the arterial wall, which significantly increases the risk of cardiovascular disease. When the authors of this study looked at the effect of vitamin E in people with this genotype, they found that it significantly decreased heart attacks and cardiovascular deaths.
This has been confirmed by a second study specifically designed to look at vitamin E supplementation in that population group (F. Micheletta et al, Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis and Vascular Biology, 24: 136, 2008). This is an example of a high-risk group benefiting from supplementation, but in this case the high risk is based on genetic variation.
Let’s look at soy and heart disease as a final example. There was a study called the ISOHEART study (W.L. Hall et al, American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 82: 1260-1268, 2005 (http://ajcn.nutrition.org/content/82/6/1260.abstract); W.L. Hall et al, American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 83: 592-600, 2006) that looked at a genetic variation in the estrogen receptor which increases inflammation and decreases levels of HDL. As you might expect, this genotype significantly increases cardiovascular risk.
Soy isoflavones significantly decrease inflammation and increase HDL levels in this population group. But they have no effect on inflammation or HDL levels in people with other genotypes affecting the estrogen reception. So, it turns out that soy has beneficial effects, but only in the population that’s at greatest risk of cardiovascular disease, and that increased risk is based on genetic variation.
These examples are just the “tip of the iceberg”. Nutrigenomics is an emerging science. New examples of genetic variations that affect the need for specific nutrients are being reported on a regular basis. We are not ready to start genotyping people yet. We don’t yet know enough to design a simple genetic test to predict our unique nutritional needs. That science is 10-20 years in the future, but this is something that’s coming down the road.
What the current studies tell us is that some people are high-risk because of their genetic makeup, and these are people for whom supplementation is going to make a significant difference. However, because genetic testing is not yet routine, most people are completely unaware that they might be at increased risk of disease or have increased nutritional requirements because of their genetic makeup.
Examples of Disease Influencing Nutritional Needs
 Finally, let’s consider the effect of disease on our nutritional needs. If you look at the popular literature, much has been written about the effect of stress on our nutritional needs. In most case, the authors are referring to psychological stress. In fact, psychological stress has relatively minor effect on our nutritional needs.
Finally, let’s consider the effect of disease on our nutritional needs. If you look at the popular literature, much has been written about the effect of stress on our nutritional needs. In most case, the authors are referring to psychological stress. In fact, psychological stress has relatively minor effect on our nutritional needs.
Metabolic stress, on the other hand, has major effects on our nutritional needs. Metabolic stress occurs when our body is struggling to overcome disease, recover from surgery, or recover from trauma. When your body is under metabolic stress, it is important to make sure your nutritional status is optimal.
The effects of surgery and trauma on nutritional needs are well documented. In my book, “Slaying The Supplement Myths”, I discussed the effects of disease on nutritional needs in some detail. Let me give you a brief overview here. It is very difficult to show beneficial effects of supplementation in a healthy population (primary prevention). However, when you look at populations that already have a disease, or are at high risk for disease, (secondary prevention), the benefits of supplementation are often evident.
For example, studies suggest that vitamin E, B vitamins, and omega-3s each may reduce heart disease risk, but only in high-risk populations. Similarly, B vitamins (folic acid, B6 and B12) appear to reduce breast cancer risk in high risk populations.
Who Benefits Most From Supplementation?
 With this information in mind, let’s return to the question: “Who benefits most from supplementation? Here is my perspective.
With this information in mind, let’s return to the question: “Who benefits most from supplementation? Here is my perspective.
1) The need for supplementation is greatest when these circles overlap, as they do for most Americans.
2) The problem is that while most of us are aware that our diets are not what they should be, we are unaware of our increased needs and/or genetic predisposition. We are also often unaware that we are at high risk of disease. For too many Americans the first indication they have heart disease is sudden death, the first indication of high blood pressure is a stroke, or the first indication of cancer is a diagnosis of stage 3 or 4 cancer.
So, let’s step back and view the whole picture. The overlapping circles are drawn that way to make a point. A poor diet doesn’t necessarily mean you have to supplement. However, when a poor diet overlaps with increased need, genetic predisposition, disease, or metabolic stress, supplementation is likely to be beneficial. The more overlapping circles you have, the greater the likely benefit you will derive from supplementation.
That is why I feel supplementation should be included along with diet, exercise, and weight control as part of a holistic approach to better health.
The Bottom Line
In this article I provide a perspective on who benefits most from supplementation and why. There are four reasons to supplement.
- Fill Nutritional gaps in our diet
2) Meet increased nutritional needs due to pregnancy, lactation, age, exercise, many common medications, and environmental pollutants.
3) Compensate for genetic variations that affect nutritional needs.
4) Overcome needs imposed by metabolic stress due to trauma, surgery, or disease.
With this information in mind, let’s return to the question: “Who benefits most from supplementation? Here is my perspective.
- A poor diet alone doesn’t necessarily mean you have to supplement. However, when a poor diet overlaps with increased need, genetic predisposition, or metabolic stress, supplementation is likely to be beneficial. The more overlap you have, the greater the likely benefit you will derive from supplementation.
2) The problem is that while most of us are aware that our diets are not what they should be, we are unaware of our increased needs and/or genetic predisposition. We are also often unaware that we are at high risk of disease. For too many Americans the first indication they have heart disease is sudden death, the first indication of high blood pressure is a stroke, or the first indication of cancer is a diagnosis of stage 3 or 4 cancer.
For more details, read the article above.
These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This information is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any disease.