Why Are Omega-3s Needed For Strong Bones?
Author: Dr. Stephen Chaney
 Osteoporosis is one of the dreaded diseases associated with aging.
Osteoporosis is one of the dreaded diseases associated with aging.
- Over 50% of women and 25% of men will develop osteoporosis in their lifetime.
And the risk of osteoporosis is highest for Caucasians.
- Over 40% of white women and 13% of white men will develop an osteoporotic fracture in their lifetime.
And osteoporotic fractures can be deadly. Bone fractures increase the risk of death 3-5-fold within the next few months. Moreover, the quality of life is diminished, and the risk of death is elevated for years after the fracture occurs.
So, if you are like many people, you are doing all you can to keep your bones strong so you will minimize your chances of developing osteoporosis. You probably even have a check list:
- Resistance exercise (strengthens the bones you pull on)……Check
- Walking (strengthens hip and leg bones)………………………Check
- Adequate calcium & vitamin D (essential for strong bones)…Check
- Magnesium & vitamin K (also important for strong bones)…..Check
- Adequate protein (Muscle pulling on bone strengthens it)…..Check
- Adequate omega-3s………………………………………………What!!!
You probably didn’t know about omega-3s. But recent research suggests they may also play a role in building strong bones and preventing osteoporosis. For example, studies show that omega-3s may influence bone metabolism by:
- Enhancing absorption of calcium from the intestine.
- Reducing the rate at which bone is broken down.
- Increasing the rate at which new bone is built.
But large-scale population studies showing that omega-3 intake influences the risk of developing osteoporosis are lacking. The study ( Z Liu et al, Frontiers In Nutrition, 11: 1467559, 2023) I am discussing today was designed to fill that gap.
But before I describe the study, I should give you a quick review of bone metabolism.
Biochemistry 101: Bone Metabolism
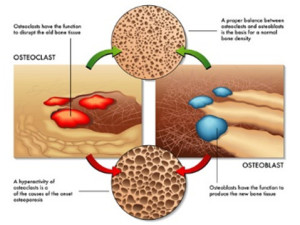 To truly understand osteoporosis and how to prevent it, you need to know a bit about bone metabolism. We tend to think of our bones as solid and unchanging, much like the steel girders supporting an office building. Nothing could be further from the truth. Our bones are dynamic organs that are in constant change throughout our lives.
To truly understand osteoporosis and how to prevent it, you need to know a bit about bone metabolism. We tend to think of our bones as solid and unchanging, much like the steel girders supporting an office building. Nothing could be further from the truth. Our bones are dynamic organs that are in constant change throughout our lives.
Cells called osteoclasts constantly break down old bone (a process called resorption), and cells called osteoblasts replace it with new bone (a process called accretion). Without this constant renewal process our bones would quickly become old and brittle.
In short, our bones are not inert. They are in constant flux. If we exercise regularly and get enough calcium, vitamin D, magnesium, and vitamin K from our diet, bone metabolism looks like this as we age.
- When we are young, osteoblast activity predominates, so accretion (the bone building process) exceeds bone resorption, and our bones grow in size and density.
- When we are adults, osteoblast and osteoclast activity are in balance. Thus, bone accretion and resorption are in balance, and our bone density stays constant. The top portion of the picture above depicts what happens when osteoclast and osteoblast activity are in balance.
- However, as we age osteoclast activity predominates, and we start to lose bone density. Eventually our bones look like Swiss cheese and break very easily. This is called osteoporosis. The bottom portion of the picture depicts this.
We should also think of our bones as calcium reservoirs. We need calcium in our bloodstream 24 hours a day for our muscles, brain, and nerves to function properly, but we only get calcium in our diet at discrete intervals. Consequently:
- When we eat our body tries to store as much calcium as possible in our bones.
- Between meals, we break down bone material so that we can release the calcium into our bloodstream that our muscle, brain & nerves need to function.
If we lead a “bone healthy” lifestyle, all of this works perfectly. We build strong bones during our growing years, maintain healthy bones during our adult years, and only lose bone density slowly as we age – maybe never experiencing osteoporosis. We always accumulate enough calcium in our bones during meals to provide for the rest of our body between meals.
I should note that this is the current paradigm for bone metabolism. The study I am discussing today is asking whether omega-3 fatty acids should also be considered as part of a bone-healthy lifestyle.
How Was This Study Done?
 The investigators used data from NHANES (National Health And Nutrition Examination Survey), an ongoing study to assess the health and nutritional status of adults and children in the United States. Specifically, this study combined data from participants from the 2005-2010, 2013-2014, and 2017-2018 NHANES surveys.
The investigators used data from NHANES (National Health And Nutrition Examination Survey), an ongoing study to assess the health and nutritional status of adults and children in the United States. Specifically, this study combined data from participants from the 2005-2010, 2013-2014, and 2017-2018 NHANES surveys.
The participants included in the survey:
- Were greater than 50 years old.
- Had completed two 24-hour dietary recall surveys to determine the omega-3 content of their diet (The average omega-3 intake of the two surveys was used for this study).
- Had a bone mineral density (BMD) test performed using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) scans.
Participants were excluded from the study if they had incomplete diet or bone mineral density data or if they had a disease that affects bone metabolism.
A total of 8,889 participants were included in the study. They were divided into 3 categories based on their bone density:
- Normal bone density (4,421 participants)
- Osteopenia (3,952 participants)
- Osteoporosis (516 participants)
Finally, the participants were divided into quartiles based on their omega-3 intake, and omega-3 intake was correlated with bone density.
Are Omega-3s Needed For Strong Bones?
 The study results were as follows:
The study results were as follows:
- Omega-3 intake was inversely related to bone density. Simply put, that means:
-
- The highest intake of omega-3s was observed in the group with normal bone density, and…
-
- The lowest omega-3 intake was observed in the osteoporosis group.
When the participants were divided into quartiles based on their omega-3 intake:
- Participants with the highest omega-3 intake were 29% less likely to develop osteoporosis than participants with the lowest omega-3 intake.
When the investigators looked at subgroups, they found stronger effects of omega-3s on osteoporosis risk for women, people under 60, and non-smokers. Specifically:
- Women with the highest omega-3 intake were 35% less likely to develop osteoporosis.
- People under 60 were 49% less likely to develop osteoporosis.
- Non-smokers were 36% less likely to develop osteoporosis.
The investigators concluded, “This study demonstrates a significant inverse relationship between dietary omega-3 fatty acid intake and osteoporosis risk, suggesting omega-3s play a crucial role in bone health. However, further longitudinal studies are needed to confirm these studies and refine dietary recommendations for osteoporosis prevention.”
Why Are Omega-3s Needed For Strong Bones?
- “Calcium and magnesium are part of bone structure. Vitamin D and vitamin K facilitate the incorporation of calcium into bone. So, it is logical that these nutrients would be important for strong bones.”
- “But what role do omega-3s play? They aren’t incorporated into bone, and they don’t affect calcium metabolism.”
Here is what the authors said about that:
- Omega-3s are anti-inflammatory. They decrease production of the pro-inflammatory cytokines that stimulate osteoclasts – the cells that break down bone.
- EPA and DHA are also converted to prostaglandins that stimulate osteoblasts – the cells that build new bone.
- Finally, the authors said, “Omega-3 fatty acids, especially EPA and DHA, have been shown to enhance calcium absorption in the gut – a process crucial for maintaining optimal bone mineral density…Omega-3s …do this by altering the lipid composition of cell membranes, thereby affecting calcium channels and enhancing calcium availability for bone tissue.”
Let me help you understand that statement.
- While we might think of our cell membranes as rigid structures, they are quite fluid. The closest analogy I can think of is a large lake. You may not see any waves or ripples, but if a leaf drops on the surface it doesn’t stay in one place. It moves. We can think of calcium channels in our membrane like leaves on the water. They move across the cell membrane.
- How fast they move depends on the fluidity of the cell membrane. This is determined by the lipids (fats) in the cell membrane, which in turn is determined by the fats in our diet. This is the one case where it is literally true that we are what we eat.
-
- When we have lots of saturated fats in our cell membranes, fluidity is low, and calcium channels move slowly across the membrane.
-
- When we have omega-3 fats in our cell membrane, fluidity is high, and calcium channels move quickly across the cell membrane.
- Calcium channels work best when they cluster together, and this works best with highly fluid, omega-3-rich cell membranes.
What Does This Mean For You?
 This study strongly suggests that omega-3s play a role in bone health, and they may be important for reducing our risk of osteoporosis. The authors concluded, “The findings suggest that omega-3 fatty acids play a critical role in bone health, supporting the need for dietary recommendations that encourage omega-3 consumption as a preventative measure against osteoporosis.”
This study strongly suggests that omega-3s play a role in bone health, and they may be important for reducing our risk of osteoporosis. The authors concluded, “The findings suggest that omega-3 fatty acids play a critical role in bone health, supporting the need for dietary recommendations that encourage omega-3 consumption as a preventative measure against osteoporosis.”
However, this is the first study of its kind, which is why the authors said, “Further longitudinal studies are needed to confirm these findings.”
However, my biggest concern with the study is that it did not include information on the intake of the other nutrients essential for bone health (calcium, vitamin D, magnesium, and vitamin K). We don’t know at present the importance of omega-3s for preventing osteoporosis relative to dietary intake of other bone-healthy nutrients. For example:
- Are omega-3s important for bone health when intake of calcium and/or the other bone-healthy nutrients are low?
- Or are omega-3s equally important for bone health under all conditions?
However, the good news is that omega-3s have many proven health benefits such as heart health, controlling blood pressure, and reducing inflammation. If they are also important for bone health, we can consider it an unexpected benefit.
With that in mind, there are two important takeaways for you:
- Omega-3s were most effective at preventing osteoporosis in people under 60. That is entirely consistent with what we know about preventing osteoporosis. The best prevention strategy is to build strong bones while you are young and maintain strong bones as long as possible in your adult years.
- The optimal reduction of osteoporosis risk in this study was seen with an omega-3 intake of 1.86 g/d. While more studies are needed to define the optimal dose of omega-3s for reducing osteoporosis risk, this dose is within the “sweet spot” for the other omega-3 benefits I mentioned.
The Bottom Line
A recent study asked whether omega-3 fatty acids reduce the risk of osteoporosis.
The study found:
- Omega-3 intake was inversely related to bone density.
- When the participants were divided into quartiles based on their omega-3 intake:
- Participants with the highest omega-3 intake were 29% less likely to develop osteoporosis than participants with the lowest omega-3 intake.
- When the investigators looked at subgroups, they found stronger effects of omega-3s on osteoporosis risk for women, people under 60, and non-smokers.
The investigators concluded, “This study demonstrates a significant inverse relationship between dietary omega-3 fatty acid intake and osteoporosis risk, suggesting omega-3s play a crucial role in bone health. This supports the need for dietary recommendations that encourage omega-3 consumption as a preventative measure against osteoporosis.”
For more information on this study, why omega-3s reduce osteoporosis risk, and what this study means for you, read the article above.
These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This information is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
_____________________________________________________________________________
My posts and “Health Tips From the Professor” articles carefully avoid claims about any brand of supplement or manufacturer of supplements. However, I am often asked by representatives of supplement companies if they can share them with their customers.
My answer is, “Yes, as long as you share only the article without any additions or alterations. In particular, you should avoid adding any mention of your company or your company’s products. If you were to do that, you could be making what the FTC and FDA consider a “misleading health claim” that could result in legal action against you and the company you represent.
For more detail about FTC regulations for health claims, see this link.
https://www.ftc.gov/business-guidance/resources/health-products-compliance-guidance
______________________________________________________________________
About The Author
 Dr. Chaney has a BS in Chemistry from Duke University and a PhD in Biochemistry from UCLA. He is Professor Emeritus from the University of North Carolina where he taught biochemistry and nutrition to medical and dental students for 40 years. Dr. Chaney won numerous teaching awards at UNC, including the Academy of Educators “Excellence in Teaching Lifetime Achievement Award”. Dr Chaney also ran an active cancer research program at UNC and published over 100 scientific articles and reviews in peer-reviewed scientific journals. In addition, he authored two chapters on nutrition in one of the leading Biochemistry textbooks for medical students.
Dr. Chaney has a BS in Chemistry from Duke University and a PhD in Biochemistry from UCLA. He is Professor Emeritus from the University of North Carolina where he taught biochemistry and nutrition to medical and dental students for 40 years. Dr. Chaney won numerous teaching awards at UNC, including the Academy of Educators “Excellence in Teaching Lifetime Achievement Award”. Dr Chaney also ran an active cancer research program at UNC and published over 100 scientific articles and reviews in peer-reviewed scientific journals. In addition, he authored two chapters on nutrition in one of the leading Biochemistry textbooks for medical students.
Since retiring from the University of North Carolina, he has been writing a weekly health blog called “Health Tips From the Professor”. He has also written two best-selling books, “Slaying the Food Myths” and “Slaying the Supplement Myths”. And most recently he has created an online lifestyle change course, “Create Your Personal Health Zone”. For more information visit https://chaneyhealth.com.
For the past 53 years Dr. Chaney and his wife Suzanne have been helping people improve their health holistically through a combination of good diet, exercise, weight control and appropriate supplementation.