How Can You Reduce Your Risk Of Breast Cancer?
Author: Dr. Stephen Chaney
 Breast cancer is scary. The good news is that treatment has gotten much better. Breast cancer is no longer a death sentence. But most women would prefer to avoid breast cancer surgery, radiation, and/or chemotherapy if they could.
Breast cancer is scary. The good news is that treatment has gotten much better. Breast cancer is no longer a death sentence. But most women would prefer to avoid breast cancer surgery, radiation, and/or chemotherapy if they could.
Could something as simple as supplementation reduce your risk of developing breast cancer? If so, which vitamins should you be taking? Or, put another way, which vitamins reduce breast cancer risk?
If you ask your doctor, they will tell you, “Supplementation is a waste of money. Vitamins don’t reduce your risk of getting cancer.” And they will be correct! That’s because these are the wrong questions.
Let me explain. These are “one size fits all” questions. Studies to answer these questions start with healthy women and asks if vitamin supplementation reduces breast cancer risk for all of them. The answer to that question is, “No”. Multiple studies have confirmed this.
But the truth is more complicated. We should be asking, “Who benefits from vitamin supplementation”, instead of, “Does everyone benefit from supplementation?”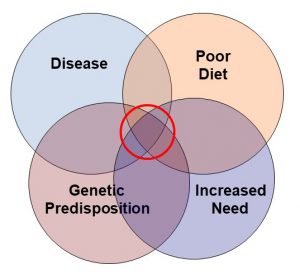
I have summed up this concept with the Venn diagram on the right. Every woman does not need supplementation. But those with poor diet, increased need, genetic predisposition, and/or certain diseases may benefit from supplementation. That is why we should be asking, “Who needs supplementation?”.
Unfortunately, while this concept of individualized treatment has led to dramatic advances for cancer drug development, it has been virtually ignored for studies on supplementation and breast cancer risk.
The current study (H Song et al., Nutrients, 14: 2644, 2022) is an exception. It asks whether obese women who wish to reduce their risk of breast may benefit more from certain micronutrients than women of normal weight.
How Was This Study Done?
 The data for this analysis came from the KoGES study. This was a study administered by the Korea Agency for Disease Control and Prevention between 2004 and 2016. It was designed to provide a scientific basis for personalized prevention of chronic diseases in the Korean population.
The data for this analysis came from the KoGES study. This was a study administered by the Korea Agency for Disease Control and Prevention between 2004 and 2016. It was designed to provide a scientific basis for personalized prevention of chronic diseases in the Korean population.
Of the 211,721 participants enrolled in the original KoGES study, this study included data from 41,593 women who:
- Underwent a health examination at 38 health examination centers upon enrollment between 2004 and 2013 and a follow up health examination between 2012 and 2016. The average follow-up period was 4.9 years.
- Were cancer-free when they enrolled in the study and developed breast cancer prior to their follow-up health examination.
- Had reliable diet data.
Dietary intake was based on a food frequency questionnaire administered during their initial health screening. Dietary intake of 15 micronutrients (calcium, phosphorous, iron, potassium, vitamin A, sodium, vitamin B1, vitamin B2, vitamin B6, niacin, folic acid, vitamin C, vitamin E, zinc, and cholesterol) and 4 macronutrients (energy, protein, fat, and carbohydrate) was determined from the food frequency data and compared to the Korean Dietary Reference Intakes (KDRIs). [Note: The Korean DRIs are slightly different than US standards.]
- The women were then divided into two groups based on whether they consumed more or less than the Korean DRIs for each nutrient.
Which Vitamins Reduce Breast Cancer Risk?
 There were two major findings from this study.
There were two major findings from this study.
1) When the investigators grouped all the women in the study together:
-
- none of the 15 micronutrients and 4 macronutrients analyzed in this study influenced breast cancer risk.
-
- This confirms most previous studies that have been designed as a “one size fits all” study. So, if your doctor was relying on this kind of study, they were technically correct in saying that vitamin supplements don’t appear to reduce breast cancer risk.
2) But when the investigators separated the women by weight, an interesting dichotomy was observed:
-
- For obese women (BMI ≥ 25 kg/m2):
-
-
- Vitamin C intake above the recommended Korean DRI (100 mg/day) reduced the risk of breast cancer by 46%.
-
-
-
- Vitamin B6 intake above the recommended Korean DRI (1.4 mg/day) reduced the risk of breast cancer by 52%.
-
-
- For women of normal weight (BMI < 25 kg/m2) neither vitamin C nor vitamin B6 had any effect on breast cancer risk.
The authors concluded, “In obese women, exceeding the recommended daily intake levels of vitamin C and vitamin B6 was associated with a lower risk of breast cancer. However, other micronutrients were not associated with breast cancer risk in these women.” [Note: Supplement use was not included in the diet survey, so above recommended intake of C and B6 was from foods consumed, not from supplements.]
What Does This Study Mean For You?
 This study is a perfect example of why we should be asking, “Who benefits from vitamin supplementation”, instead of, “Does everyone benefit from supplementation?”
This study is a perfect example of why we should be asking, “Who benefits from vitamin supplementation”, instead of, “Does everyone benefit from supplementation?”
In terms of the Venn diagram I introduced above, some people consider obesity a disease.
But whether you consider obesity a disease or not, it does increase the need for many nutrients. So, it is conceivable that extra vitamins C and B6 might provide benefits in obese women that are not seen in non-obese women.
This is, of course, a ground-breaking study. It is the first study of its kind and deserves to be followed by other studies to confirm this observation. Ideally, these studies would test whether the same effect is seen in other population groups and determine the optimal dose of vitamin C and B6 to reduce breast cancer risk.
However, I am not optimistic that these studies will be done. It is easy to get funding for the “do vitamin supplements benefit everyone?” studies that confirm the existing prejudice against vitamin supplementation.
It is much harder to obtain funding for “who benefits from vitamin supplementation?” studies that challenge the existing paradigm. But these are the kind of studies that are needed most.
How Can You Reduce Your Risk Of Breast Cancer?
 As I said, this is the first study of its kind, so you could consider the results as preliminary. However, assuming it might be true:
As I said, this is the first study of its kind, so you could consider the results as preliminary. However, assuming it might be true:
- I do not recommend megadoses of vitamins C and B6. The above average intake of C and B6 in this study came from food alone. And we do not have any dose response studies that might define an optimal dose of C and B6.
- I do recommend balance. Based on this study, multivitamins should provide enough C and B6 to have a meaningful effect on breast cancer risk. And multivitamins are inexpensive and risk-free.
In addition, there are things you can do that are proven to reduce breast cancer risk. Here is what the American Cancer Society recommends:
- Get to and stay at a healthy weight.
- Be physically active and avoid time sitting.
- Follow a healthy eating plan.
- It is best not to drink alcohol.
- Think carefully about using hormone replacement therapy.
I provide more detail about each of these recommendations in a recent article in “Health Tips From the Professor”.
The Bottom Line
Most doctors will tell you that supplementation does not reduce your risk of breast cancer. And that opinion is backed up by multiple published clinical studies.
But the problem is that these studies are all asking the wrong question. They are asking, “Does supplementation reduce the risk of breast cancer for all women?”. A better question would be, “Which women benefit from supplementation?”
A recent study asked both of those questions. They looked at the effect of 15 micronutrients on breast cancer risk.
- When the investigators grouped all the women in the study together:
-
- None of the 15 micronutrients influenced breast cancer risk.
2) But when the investigators separated the women by weight, an interesting dichotomy was observed:
-
- For obese women (BMI ≥ 25 kg/m2):
-
-
- Vitamin C intake above the recommended intake reduced the risk of breast cancer by 46%.
-
-
-
- Vitamin B6 intake above the recommended intake reduced the risk of breast cancer by 52%.
-
-
- For women of normal weight (BMI < 25 kg/m2) neither vitamin C nor vitamin B6 had any effect on breast cancer risk.
The authors concluded, “In obese women, exceeding the recommended daily intake levels of vitamin C and vitamin B6 was associated with a lower risk of breast cancer. However, other micronutrients were not associated with breast cancer risk in these women.”
For more information on this study, what it means for you, and proven methods for reducing breast cancer risk read the article above.
These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This information is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
____________________________________________________________________________
My posts and “Health Tips From the Professor” articles carefully avoid claims about any brand of supplement or manufacturer of supplements. However, I am often asked by representatives of supplement companies if they can share them with their customers.
My answer is, “Yes, as long as you share only the article without any additions or alterations. In particular, you should avoid adding any mention of your company or your company’s products. If you were to do that, you could be making what the FTC and FDA consider a “misleading health claim” that could result in legal action against you and the company you represent.
For more detail about FTC regulations for health claims, see this link.
https://www.ftc.gov/business-guidance/resources/health-products-compliance-guidance